Optimizing O red blood cell concentrate usage in the emergency department in the era of patient blood management
- PMID: 39183144
- PMCID: PMC11670554
- DOI: 10.1016/j.htct.2024.05.008
Optimizing O red blood cell concentrate usage in the emergency department in the era of patient blood management
Abstract
Background: Emergency transfusion may require the availability of O-negative red blood cell concentrates without pre-transfusion testing. At the Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc, the emergency department was used to having access to two decentralized O-negative red blood cell concentrates. This study aims to analyze the consumption of O-negative red blood cell concentrates in emergency situations both before and after the implementation of a novel strategy aiming at optimizing stocks. This strategy provides a combined allocation of one unit of O-positive red blood cell concentrate and one unit of O-negative red blood cell concentrate decentralized in the emergency department and reserve the transfusion of the negative unit only to under 45-year-old women and under 20-year-old men.
Materials and methods: A retrospective study was conducted of the transfusion and medical records of all patients who received immediate transfusions in the emergency department without pre-transfusion testing between 2008 and 2022.
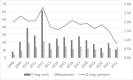
Results: A total of 193 patients received O red blood cell concentrates without pre-transfusion testing in emergency situations between 2008 and 2022. During the first 24 h of hospitalization, 354 O-negative units were transfused. Mean ratios of number of O-negative bags between 2008 and 2020 was 1.98 unit/patient. After implementation of the new strategy, the ratio in 2021 was 1.46 unit/patient and drastically decreased in 2022 to 0.79 unit/patient.
Conclusion: In situations of emergency, allocating O-negative units only for women younger than 45 years and men younger than 20 years could have saved 85% of O-negative red blood cell concentrates transfused (303/354) yet balancing the immunological risk. Limiting the number of delocalized units of O-negative red blood cell concentrates in the emergency department seems to lower O-negative consumption. With this strategy, the units spared could have been transfused to patients with greater needs (e.g., sickle cell patients or chronically transfused patients).
Keywords: Emergency department; O-negative red blood cells; Patient blood management; Uncrossmatched transfusion.
Copyright © 2024 Associação Brasileira de Hematologia, Hemoterapia e Terapia Celular. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors affirm that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Standards for Blood Banks and Transfusion Services, 33rd edition—Print. (n.d.). Aabb.Org. Retrieved July 25, 2023, from https://www.aabb.org/aabb-store/product/standards-for-blood-banks-and-tr...
-
- Zatta A.J., McQuilten Z.K., Mitra B., Roxby D.J., Sinha R., Whitehead S., Dunkley S., Kelleher S., Hurn C., Cameron P.A., Isbister J.P., Wood E.M., Phillips L.E., Massive Transfusion Registry Steering Committee Elucidating the clinical characteristics of patients captured using different definitions of massive transfusion. Vox Sang. 2014;107(1):60–70. doi: 10.1111/vox.12121. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Streel, C., Pouplard, M., Laporte, F., Bertrand, O., Luyten, U., Pirlet, C., Khaouch, Y., & Deneys, V. (2023). There is an urgent need to adopt a pull-flow logic for the supply of RBCs to meet patients’ needs: A single center study. Transfusion Clinique Et Biologique: Journal De La Societe Francaise De Transfusion Sanguine, S1246-7820(23)00073-3. 10.1016/j.tracli.2023.06.008 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources