No evidence that ACE2 or TMPRSS2 drive population disparity in COVID risks
- PMID: 39183295
- PMCID: PMC11346279
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03539-0
No evidence that ACE2 or TMPRSS2 drive population disparity in COVID risks
Abstract
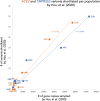
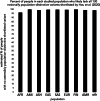
Early in the SARS-CoV2 pandemic, in this journal, Hou et al. (BMC Med 18:216, 2020) interpreted public genotype data, run through functional prediction tools, as suggesting that members of particular human populations carry potentially COVID-risk-increasing variants in genes ACE2 and TMPRSS2 far more often than do members of other populations. Beyond resting on predictions rather than clinical outcomes, and focusing on variants too rare to typify population members even jointly, their claim mistook a well known artifact (that large samples reveal more of a population's variants than do small samples) as if showing real and congruent population differences for the two genes, rather than lopsided population sampling in their shared source data. We explain that artifact, and contrast it with empirical findings, now ample, that other loci shape personal COVID risks far more significantly than do ACE2 and TMPRSS2-and that variation in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 per se unlikely exacerbates any net population disparity in the effects of such more risk-informative loci.
Keywords: ACE2; TMPRSS2; COVID; COVID19; Functional prediction; GWAS; Host genetics; Human genes; Immunity; Infection; Polygenic risk; Population genetics; Population structure; Rare variants; SARS-CoV2; Sample design; Sample size; Sampling.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

