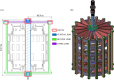
The magnetic cage
- PMID: 39183661
- PMCID: PMC11423674
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0407
The magnetic cage
Abstract
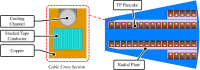
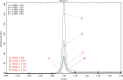
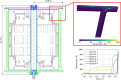
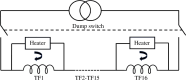
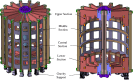
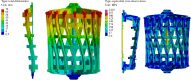
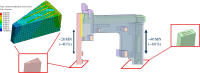
The Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP) requires high-field magnet designs and has therefore adopted the REBCO-based high-temperature superconductor (HTS) as its current carrier. The HTS enables the toroidal field (TF) coils to be remountable, which unlocks STEP's vertical maintenance approach; however, remountable joints, approximately 18 GJ of stored energy and limited space down the centre of a spherical tokamak, make the TF coils the most challenging. STEP has pursued a passive approach to TF coil quench protection in order to limit coil terminal voltage. Initial results suggest that a solution may rely on tuning internal coil resistance coupled with actively powered heaters. The pre-conceptual inter-coil structure demonstrates acceptable stresses and deflections under steady-state operating conditions and preliminary fault scenarios, and loads are distributed to limit the tensile force on the TF centre rod. Finally, the HTS must operate reliably in a high radiation environment and endure high neutron fluences, ensuring commercially relevant magnet lifetimes. Initial experiments indicate that instantaneous gamma irradiation of HTS has no negative impact on current carrying capacity. Experimental programmes are underway to cold irradiate HTS to fusion-relevant fluences and to develop a method of assuring tape irradiation tolerance using oxygen ions as an analogue for neutrons.This article is part of the theme issue 'Delivering Fusion Energy - The Spherical Tokamak for Energy Production (STEP)'.
Keywords: HTS; REBCO; STEP; magnet; quench; superconductor.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hashizume H, Kitajima S, Ito S, Yagi K, Usui Y, Hida Y, Sagara A. 2002. Advanced fusion reactor design using remountable HTc SC magnet. J. Plasma Fusion Res. Ser. 5 , 532–536.
-
- Ito S, Bromberg L, Takayasu M, Minervini JV, Hashizume H. 2012. Proposal of electrical edge joint for a demountable high-temperature Superconducting magnet. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40 , 1446–1452. (10.1109/TPS.2012.2190103) - DOI
-
- Zhai Y, Larbalestier D, Duckworth R, Hartwig Z, Prestemon S, Forest C. 2024. R&D needs for a U.S. fusion magnet base program. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 34 , 4200705. (10.1109/TASC.2023.3349368) - DOI
-
- Hartwig ZS, et al. . 2024. The SPARC toroidal field model coil program. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 34 , 1–16. (10.1109/TASC.2023.3332613) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
