Impact of Subclinical Hypothyroidism on Lipid Profile in Jeddah: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 39184696
- PMCID: PMC11345027
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.65433
Impact of Subclinical Hypothyroidism on Lipid Profile in Jeddah: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
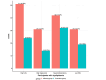
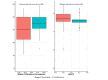
Background Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) have a high serum concentration of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), whereas their serum-free thyroxine concentrations are normal. Lipid metabolism is regulated in large part by thyroid hormones. It could be connected to a changed lipid profile. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between SCH and alterations in the lipid profile. Methodology Data from 99 patients with SCH and 109 euthyroid cases were collected from King Abdulaziz Medical City, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, from 2016 to 2022. Patients older than 18 years were included in the study. The groups were matched in terms of gender, age, and body mass index. SCH was defined as a TSH value of 4.5 to 10 mIU/L, and normal T4 as 5 to 18 μg/dL. Control cases had a normal TSH ranging from 0.45 to 4.5 mIU/L. The total serum cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglyceride (TG) levels in both groups were examined and the results were recorded. Results In comparison to the control group, SCH patients had greater median glycated hemoglobin (HbA1C) (p = 0.001) and lower median vitamin D levels (p = 0.004) before therapy. Before therapy, SCH patients also showed considerably lower HDL levels and significantly higher LDL and TG levels (p < 0.001). Conclusions There is a substantial correlation between SCH and reduced HDL and vitamin D levels. It was linked to increased TG, LDL, and HbA1c levels. Only vitamin D and LDL were pathologically high. Treatment with levothyroxine raised total and LDL cholesterol levels. Future research should look into the affordability of treating SCH.
Keywords: hypothyroidism; lipids; low-density lipoprotein (ldl); subclinical; subclinical hypothyroidism; thyroid.
Copyright © 2024, Alzahrani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Institutional Review Board, King Abdullah International Medical Research Center issued approval NRJ23J/228/09. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation Between Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Dyslipidemia.Iran J Pathol. 2017 Spring;12(2):106-111. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Iran J Pathol. 2017. PMID: 29515631 Free PMC article.
-
A Study of Lipid Profile in Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism.J Assoc Physicians India. 2022 Apr;70(4):11-12. J Assoc Physicians India. 2022. PMID: 35443331
-
Evaluation response and effectiveness of thyroid hormone replacement treatment on lipid profile and function in elderly patients with subclinical hypothyroidism.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2007 Jan-Feb;44(1):13-9. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2006.01.006. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2007. PMID: 16621071
-
Effect of Levothyroxine on Older Patients With Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 14;13:913749. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.913749. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35909574 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Thyroid Dysfunction and Serum Lipids: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Dec 1;105(12):dgaa672. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa672. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32954428
Cited by
-
Exploring hypothyroidism's effects on lipid profiles: Evidence of metabolic consequences in subclinical disease.Saudi Med J. 2025 May;46(5):491-496. doi: 10.15537/smj.2025.46.5.20241147. Saudi Med J. 2025. PMID: 40335115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hyperlipidemia in patients with primary and secondary hypothyroidism. O'Brien T, Dinneen SF, O'Brien PC, Palumbo PJ. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993;68:860–866. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
