The Clinical, Radiological and Genetic Spectrum of PLA2G6-Associated Neurodegeneration: An Experience From a Tertiary Center
- PMID: 39184971
- PMCID: PMC11342831
- DOI: 10.5334/tohm.897
The Clinical, Radiological and Genetic Spectrum of PLA2G6-Associated Neurodegeneration: An Experience From a Tertiary Center
Abstract
Background: Despite being the second most common type of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation, there is limited literature on PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration (PLAN) within the Asian ethnicity, particularly in the Indian context.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational study on patients with pathogenic/likely pathogenic PLA2G6 variants based on exome sequencing.
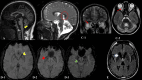
Results: We identified 26 patients (22 families, 15 males) of genetically-confirmed PLAN with a median age of 22.5 years and age at onset of 13.0 years, encompassing various subtypes: infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (5/26;19.2%), atypical neuroaxonal dystrophy (3/26;11.5%), dystonia-parkinsonism (5/26;19.2%), dystonia-parkinsonism-myoclonus (n = 4, 15.38%), early-onset Parkinson's disease (2/26;7.7%), complex dystonia (2/26;7.7%), and complicated hereditary spastic paraparesis (cHSP; 5/26;19.2%). The common initial symptoms included walking difficulty (7/26;26.9%), developmental regression (6/26;23.1%), and slowness (4/26;15.4%). Dystonia (14/26;53.8%), followed by parkinsonism (11/26; 42.3%), was the most common motor symptom. Non-motor symptoms included cognitive decline (12/26;46.2%) and behavioral changes (6/26;23.1%). Neuroimaging revealed cerebellar atrophy in 23/26 (88.5%) patients and claval hypertrophy in 80% (4/5) of INAD patients. Levodopa responsiveness was noted in 12 of 14 patients with parkinsonism/dystonia who received levodopa, and dyskinesia was noted in 10/11 patients. Genetic analysis revealed a total of 19 unique variants in PLA2G6 gene, of which 11 were novel. Twelve patients harbored the c.2222G>A variant, which is predominantly seen in Asian subpopulations.
Conclusions: The study introduces 26 new patients of PLAN and 12 patients associated with the c.2222G>A variant, potentially forming the most extensive single center series to date. It also expands the phenotypic, neuroimaging, and genotypic spectrum of PLAN.
Keywords: ANAD; Dystonia; HSP; INAD; PLA2G6; PLAN; early-onset Parkinson’s disease.
Copyright: © 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Shaikh HR, Milanowski LM, Holla VV, Kurihara K, Yadav R, Kamble N, Muthusamy B, Bellad A, Koziorowski D, Szlufik S, Hoffman-Zacharska D, Fujioka S, Tsuboi Y, Ross OA, Wierenga K, Uitti RJ, Wszolek Z, Pal PK. PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration in four different populations-case series and literature review. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2022; 101: 66–74. DOI: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.06.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet. 2011; 43(5): 491–8. DOI: 10.1038/ng.806 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

