Use of dupilumab for recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid: A case report
- PMID: 39185064
- PMCID: PMC11342423
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X241274855
Use of dupilumab for recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid: A case report
Abstract
Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune blistering disease affecting the dermo-epidermal junction, most commonly seen in older patients. First-line treatment includes systemic, topical corticosteroids and/or steroid-sparing immunosuppressants. Treatment with these medications may be limited by their safety profile. Dupilumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 cytokines currently indicated for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, severe asthma, chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis, and moderate-to-severe prurigo nodularis. We report a case of a patient with recalcitrant bullous pemphigoid effectively treated with dupilumab.
Keywords: Bullous pemphigoid; biologics; bullous disease; dupilumab.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
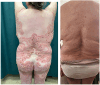


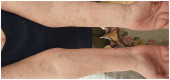
References
-
- Yang J, Gao H, Zhang Z, et al.. Dupilumab combined with low-dose systemic steroid therapy improves efficacy and safety for bullous pemphigoid. Dermatol Ther 2022; 35(8): e15648. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Man X, Tang Z, et al.. Dupilumab as a novel therapy for bullous pemphigoid. Int J Dermatol 2023; 62(4): e263–e266. - PubMed
-
- Napolitano M, Di Guida A, Nocerino M, et al.. The emerging role of dupilumab in dermatological indications. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2021; 21(11): 1461–1471. - PubMed
-
- Lin Z, Zhao Y, Li F, et al.. Efficacy and safety of biological agents for pemphigoid: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol 2023; 62(8): 1000–1008. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

