Alzheimer's disease: a review on the current trends of the effective diagnosis and therapeutics
- PMID: 39185459
- PMCID: PMC11341404
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1429211
Alzheimer's disease: a review on the current trends of the effective diagnosis and therapeutics
Abstract
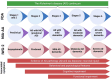
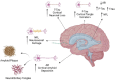
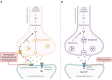
The most prevalent cause of dementia is Alzheimer's disease. Cognitive decline and accelerating memory loss characterize it. Alzheimer's disease advances sequentially, starting with preclinical stages, followed by mild cognitive and/or behavioral impairment, and ultimately leading to Alzheimer's disease dementia. In recent years, healthcare providers have been advised to make an earlier diagnosis of Alzheimer's, prior to individuals developing Alzheimer's disease dementia. Regrettably, the identification of early-stage Alzheimer's disease in clinical settings can be arduous due to the tendency of patients and healthcare providers to disregard symptoms as typical signs of aging. Therefore, accurate and prompt diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease is essential in order to facilitate the development of disease-modifying and secondary preventive therapies prior to the onset of symptoms. There has been a notable shift in the goal of the diagnosis process, transitioning from merely confirming the presence of symptomatic AD to recognizing the illness in its early, asymptomatic phases. Understanding the evolution of disease-modifying therapies and putting effective diagnostic and therapeutic management into practice requires an understanding of this concept. The outcomes of this study will enhance in-depth knowledge of the current status of Alzheimer's disease's diagnosis and treatment, justifying the necessity for the quest for potential novel biomarkers that can contribute to determining the stage of the disease, particularly in its earliest stages. Interestingly, latest clinical trial status on pharmacological agents, the nonpharmacological treatments such as behavior modification, exercise, and cognitive training as well as alternative approach on phytochemicals as neuroprotective agents have been covered in detailed.
Keywords: AD; Alzheimer’s disease; clinical trial; dementia; diagnosis; treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Abdul Manap, Almadodi, Sultana, Sebastian, Kavani, Lyenouq and Shankar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- A Mental Workout (2023). Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. Available online at: https://alz.org/news/2020/a-mental-workout (accessed November 05, 2023).
-
- Abdul Manap A., Vijayabalan S., Madhavan P., Chia Y., Arya A., Wong E., et al. (2019a). Bacopa monnieri, a Neuroprotective Lead in Alzheimer disease: A review on its properties, mechanisms of action, and preclinical and clinical studies. Drug Target Insights 13:1177392819866412. 10.1177/1177392819866412 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdul Manap A., Wei Tan A., Leong W., Yin Chia A., Vijayabalan S., Arya A., et al. (2019b). Synergistic effects of curcumin and piperine as potent acetylcholine and amyloidogenic inhibitors with significant neuroprotective activity in SH-SY5Y cells via computational molecular modeling and in vitro assay. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:206. 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00206 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abushakra S., Porsteinsson A., Vellas B., Cummings J., Gauthier S., Hey J., et al. (2016). Clinical benefits of tramiprosate in Alzheimer’s disease are associated with higher number of APOE4 alleles: The “APOE4 gene-dose effect.” J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 3 219–228. 10.14283/jpad.2016.115 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

