The effectiveness of live music in reducing anxiety and depression among patients undergoing haemodialysis. A randomised controlled pilot study
- PMID: 39186740
- PMCID: PMC11346941
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307661
The effectiveness of live music in reducing anxiety and depression among patients undergoing haemodialysis. A randomised controlled pilot study
Abstract
Background: Anxiety and depression are highly prevalent disorders among individuals undergoing chronic haemodialysis. For patients with kidney disease, the haemodialysis process often exacerbates these conditions. This study aims to investigate the effects of listening to live classical music on anxiety and depression scales during haemodialysis sessions.
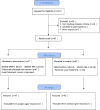
Methods: A randomised clinical trial was conducted with a group of patients who listened to live classical music during haemodialysis sessions, while the control group received treatment as usual. Anxiety and depression levels were assessed at baseline and after 4 weeks of listening to live music. The study comprised 90 patients.
Results: The results demonstrated a significant decrease in anxiety and depression among the intervention group, who listened to music, compared to the control group, who did not receive this intervention. Specifically, the intervention group, presented a decrease in score on the anxiety scale of -5.35 (p < 0.001) points on average and a decrease in score on the depression scale of -5.88 (p < 0.001) points on average, while in the control group the levels worsened with the progression of time.
Conclusion: It is concluded that listening to live classical music during haemodialysis sessions reduces anxiety and depression levels in HD patients. This conclusion adds value to listening to live music in the hospital context, specifically in this case, in haemodialysis rooms.
Copyright: © 2024 Soliva et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Peña Martínez B. Anxiety and depression in kidney patients.[Final degree project]. Cantabria: UC 2019.
-
- Merino Martínez RM, Morillo Gallego N, Sánchez Cabezas AM, Gómez López VE, Crespo Montero R. Relationship between health-related quality of life and anxiety/depression in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Enferm Nephrol [Internet]. 2019;22(3):274–83. Available from: 10.4321/s2254-28842019000300006 - DOI
-
- Ayala Servin JN. Evaluation of the state of anxiety and depression of patients with chronic renal failure at the Hospital de Clínicas. Scientific Journal UPAP [Internet]. 2021;1(1):27–36. Available from: 10.54360/rcupap.v1i1.6 - DOI