Tau is required for glial lipid droplet formation and resistance to neuronal oxidative stress
- PMID: 39187706
- PMCID: PMC11809452
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-024-01740-1
Tau is required for glial lipid droplet formation and resistance to neuronal oxidative stress
Abstract
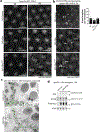
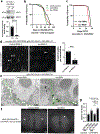
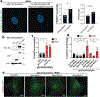
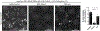
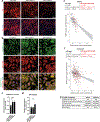
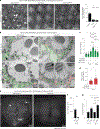
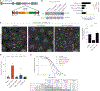
The accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is a common feature of tauopathies, defined by Tau accumulations in neurons and glia. High ROS in neurons causes lipid production and the export of toxic peroxidated lipids (LPOs). Glia uptake these LPOs and incorporate them into lipid droplets (LDs) for storage and catabolism. We found that overexpressing Tau in glia disrupts LDs in flies and rat neuron-astrocyte co-cultures, sensitizing the glia to toxic, neuronal LPOs. Using a new fly tau loss-of-function allele and RNA-mediated interference, we found that endogenous Tau is required for glial LD formation and protection against neuronal LPOs. Similarly, endogenous Tau is required in rat astrocytes and human oligodendrocyte-like cells for LD formation and the breakdown of LPOs. Behaviorally, flies lacking glial Tau have decreased lifespans and motor defects that are rescuable by administering the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine amide. Overall, this work provides insights into the important role that Tau has in glia to mitigate ROS in the brain.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



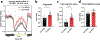






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021-00027/Canada Research Chairs (Chaires de recherche du Canada)
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 OD031447/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD024064/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080820/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG017216/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018023/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG072439/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK129815/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P40 OD018537/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD083092/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032990/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS043124/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067858/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32-NS043124-18/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R01 AG073260/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG078660/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 OD022005/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025711/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD103555/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

