A Case of Primary Hepatic Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma in a Patient With Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- PMID: 39188441
- PMCID: PMC11345519
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.65472
A Case of Primary Hepatic Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma in a Patient With Primary Biliary Cholangitis and Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Abstract
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma is a low-grade malignant lymphoproliferative disease, representing a low percentage of newly diagnosed lymphoma cases. Although its exact cause is still unclear, it is commonly associated with infections or autoimmune diseases. The stomach is the most frequent site for MALT lymphoma, with primary hepatic MALT lymphoma being exceptionally rare. Cases of primary hepatic MALT lymphoma often coincide with viral hepatitis. In this report, we present a case of primary hepatic MALT lymphoma in a patient with no history of hepatitis but complicated by primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Keywords: hashimoto's thyroiditis; hypothyroidism; management; mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (malt) lymphoma; primary biliary cholangitis.
Copyright © 2024, Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
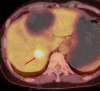

References
-
- Clinicopathologic characteristics and treatment of marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT lymphoma) Raderer M, Kiesewetter B, Ferreri AJ. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:153–171. - PubMed
-
- The aetiology of B-cell lymphoid malignancies with a focus on chronic inflammation and infections. Smedby KE, Ponzoni M. J Intern Med. 2017;282:360–370. - PubMed
-
- Chronic inflammation and extra-nodal marginal-zone lymphomas of MALT-type. Thieblemont C, Bertoni F, Copie-Bergman C, Ferreri AJ, Ponzoni M. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;24:33–42. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
