mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated Restoration of PTPN14 Exhibits Antitumor Effects by Overcoming Anoikis Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39189475
- PMCID: PMC11348215
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202309988
mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated Restoration of PTPN14 Exhibits Antitumor Effects by Overcoming Anoikis Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
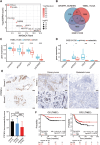
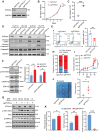
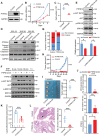
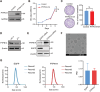
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) poses a challenging prognosis due to early metastasis driven by anoikis resistance. Identifying crucial regulators to overcome this resistance is vital for improving patient outcomes. In this study, a genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screen in TNBC cells has identified tyrosine-protein phosphatase nonreceptor type 14 (PTPN14) as a key regulator of anoikis resistance. PTPN14 expression has shown a progressive decrease from normal breast tissue to metastatic tumors. Overexpressing PTPN14 has induced anoikis and inhibited cell proliferation in TNBC cells, while normal human breast cells are unaffected. Mechanistically, PTPN14 is identified as a key factor in dephosphorylating breast cancer antiestrogen resistance 3, a novel substrate, leading to the subsequent inhibition of PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Local delivery of in vitro transcribed PTPN14 mRNA encapsulated by lipid nanoparticles in a TNBC mouse model has effectively inhibited tumor growth and metastasis, prolonging survival. The study underscores PTPN14 as a potential therapeutic target for metastatic TNBC, with the therapeutic strategy based on mRNA expression of PTPN14 demonstrating clinical application prospects in alleviating the burden of both primary tumors and metastatic disease.
Keywords: PTPN14; anoikis resistance; cancer therapy; mRNA therapeutics; triple‐negative breast cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F., CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209. - PubMed
-
- a) Lin N. U., Vanderplas A., Hughes M. E., Theriault R. L., Edge S. B., Wong Y. N., Blayney D. W., Niland J. C., Winer E. P., Weeks J. C., Cancer 2012, 118, 5463; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Prat A., Lluch A., Albanell J., Barry W. T., Fan C., Chacon J. I., Parker J. S., Calvo L., Plazaola A., Arcusa A., Segui‐Palmer M. A., Burgues O., Ribelles N., Rodriguez‐Lescure A., Guerrero A., Ruiz‐Borrego M., Munarriz B., Lopez J. A., Adamo B., Cheang M. C., Li Y., Hu Z., Gulley M. L., Vidal M. J., Pitcher B. N., Liu M. C., Citron M. L., Ellis M. J., Mardis E., Vickery T., et al., Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1532; - PMC - PubMed
- c) Borri F., Granaglia A., Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 72, 136. - PubMed
-
- Gilmore A. P., Cell Death Differ. 2005, 2, 1473. - PubMed
-
- a) Marcotte R., Sayad A., Brown K. R., Sanchez‐Garcia F., Reimand J., Haider M., Virtanen C., Bradner J. E., Bader G. D., Mills G. B., Pe'er D., Moffat J., Neel B. G., Cell 2016, 164, 293; - PMC - PubMed
- b) Tsherniak A., Vazquez F., Montgomery P. G., Weir B. A., Kryukov G., Cowley G. S., Gill S., Harrington W. F., Pantel S., Krill‐Burger J. M., Meyers R. M., Ali L., Goodale A., Lee Y., Jiang G., Hsiao J., Gerath W. F. J., Howell S., Merkel E., Ghandi M., Garraway L. A., Root D. E., Golub T. R., Boehm J. S., Hahn W. C., Cell 2017, 170, 564. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
