Long-term results of treatment of Gustilo-Anderson type 3A-B tibia fractures due to combat-related high-energy ballistic injuries treated with external circular fixator: Experience of the Military Medical Academy
- PMID: 39189574
- PMCID: PMC11411876
- DOI: 10.52312/jdrs.2024.1797
Long-term results of treatment of Gustilo-Anderson type 3A-B tibia fractures due to combat-related high-energy ballistic injuries treated with external circular fixator: Experience of the Military Medical Academy
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the longterm outcomes of open tibia fractures treated using the Ilizarov external circular fixation (ECF) technique in the Military Medical Academy.
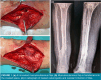
Patients and methods: Between January 1992 and December 2011, a total of 134 male military personnel (median age: 22.5 years; range, 18 to 36 years) with Gustilo-Anderson type 3 open tibia fractures treated with ECF were retrospectively analyzed. All patients underwent multiple surgeries and eventually Ilizarov fixation surgery. The radiological and functional outcomes were evaluated using the Association for the Study and Application of Methods of Ilizarov (ASAMI) criteria, and complications were noted.
Results: The median follow-up was 17.7 (range, 10 to 29) years. The median time to union was 4.7 (range, 3 to 8) months. All frames were removed from the limb, when union was observed. No re-fracture, limb length discrepancy more than 2.5 cm, or below-knee amputation after Ilizarov treatment was seen in any patient. Chronic osteomyelitis was observed at in 40% (n=54) of the patients at a median time ranging from 17 to 148 months. The overall ASAMI bone scores were excellent in 40 (30%), good in 20 (15%), fair in 20 (15%), and poor in 54 (40%) patients with osteomyelitis. The ASAMI functional scores were excellent in 40 (30%), good in 40 (30%), and fair in 54 patients (40%). No poor score was observed. Minor pin site infections were observed in 63 patients (47%).
Conclusion: Our long-term study results showed that all patients returned to their social life and were mobilized without support after treatment with the use of Ilizarov ECF method of open tibia fractures caused by high-energy ballistic injuries. However, complications such as pin tract infections and osteomyelitis after several years must be kept in mind in the treatment of comminuted bone fractures caused by firearms and ballistic missiles injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Atesalp AS, Yildiz C, Başbozkurt M, Gür E. Treatment of type IIIa open fractures with Ilizarov fixation and delayed primary closure in high-velocity gunshot wounds. Mil Med. 2002;167:56–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

