High-grade B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: CNS involvement and outcomes in a multi-institutional series
- PMID: 39189932
- PMCID: PMC11568788
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013791
High-grade B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: CNS involvement and outcomes in a multi-institutional series
Abstract
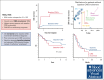
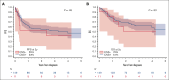
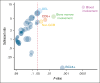
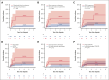
Little is known about the central nervous system (CNS) risk in high-grade B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (HGBL NOS). Hence, we sought to describe the rates of baseline CNS involvement, risk of CNS recurrence after primary therapy, and management strategies in HGBL NOS. In this multicenter retrospective study, we included 160 adults with newly diagnosed HGBL NOS treated between 2016 and 2021 at 20 US institutions. Eleven patients (7%) had baseline CNS involvement at diagnosis (leptomeningeal = 6, parenchymal = 4, and both = 1). Baseline CNS involvement was significantly associated only with MYC rearrangement (OR = 3.5) and testicular (in men) or female pelvic (in women) involvement (OR = 8.1). There was no significant difference in survival outcomes between patients with HGBL NOS with (median PFS = 4 years) or without (median PFS = 2.4 years) baseline CNS involvement (P = 0.45). The cumulative incidence of CNS recurrence at 3 years was 11%. Patients with baseline CNS involvement were at the highest risk (48.5% vs 8% for those without baseline CNS involvement) and were excluded from the risk factors analysis for CNS recurrence. The risk for CNS recurrence was significantly associated with blood or bone marrow involvement, CD5 expression, non-germinal center B-cell subtype, and "dual-expresser lymphoma" phenotype, however, high CNS IPI was not. The prognosis of relapsed HGBL NOS was poor, regardless of whether recurrence was systemic or limited to the CNS, and with currently available salvage strategies, including autologous transplantation and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell modalities, almost all patients with CNS recurrence ultimately succumbed to their disease.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: N.E. reports research funding from BeiGene and Eli Lilly; serves on the speaker's bureau for BeiGene and Genentech; serves on advisory boards for Ipsen, Lilly, and ADC Therapeutics; and reports consultancy for Novartis. R.K. serves in a consultant role for Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, MorphoSys/Incyte, Epizyme, Genentech/Roche, GenMab, Lilly Oncology, AbbVie, and Miltenyi; reports grants/research support from Bristol Myers Squibb, Takeda, BeiGene, Gilead Sciences/Kite, and Miltenyi; and serves on the speakers' bureau for AstraZeneca, BeiGene, and Incyte. P.T. reports honoraria, consulting roles, and advisory board membership for TG Therapeutics, ADC Therapeutics, Genentech, GenMab, Seagen, AbbVie, and Lilly USA. A.J.O. reports research funding from Genmab, Precision Bio, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Celldex, Acrotech Biopharma, Schrodinger, TG Therapeutics, and Genentech. M.L.X. reports consulting roles for Pure Marrow and Treeline Biosciences. D.A.B. reports consulting roles for Novartis, Nurix Therapeutics, and ADC Therapeutics, and and received research funding from Novartis, Nurix Therapeutics, Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genmab, and Accutar Biotechnology. A.M.B. reports honoraria and advisory board membership for AbbVie. M.K. reports research support/funding from Novartis; consultancy with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, BeiGene, and Genentech; and serves on the speakers' bureau of Seagen, Celgene, and Genentech. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kansara R, Villa D, Gerrie AS, et al. Site of central nervous system (CNS) relapse in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) by the CNS-IPI risk model. Br J Haematol. 2017;179(3):508–510. - PubMed
-
- Ferreri AJ, Donadoni G, Cabras MG, et al. High doses of antimetabolites followed by high-dose sequential chemoimmunotherapy and autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with systemic B-cell lymphoma and secondary CNS involvement: final results of a Multicenter Phase II Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(33):3903–3910. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

