Lung megakaryocytes engulf inhaled airborne particles to promote intrapulmonary inflammation and extrapulmonary distribution
- PMID: 39191805
- PMCID: PMC11349891
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51686-y
Lung megakaryocytes engulf inhaled airborne particles to promote intrapulmonary inflammation and extrapulmonary distribution
Abstract
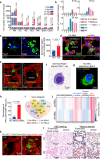
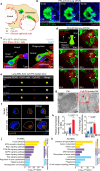
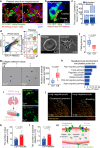
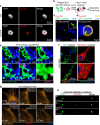
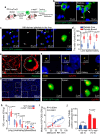
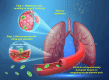
Many lung immune cells are known to respond to inhaled particulate matter. However, current known responses cannot explain how particles induce thrombosis in the lung and how they translocate to distant organs. Here, we demonstrate that lung megakaryocytes (MKs) in the alveolar and interstitial regions display location-determined characteristics and act as crucial responders to inhaled particles. They move rapidly to engulf particles and become activated with upregulation in inflammatory responses and thrombopoiesis. Comprehensive in vivo, in vitro and ex vivo results unraveled that MKs were involved in particle-induced lung damages and shed particle-containing platelets into blood circulation. Moreover, MK-derived platelets exhibited faster clotting, stronger adhesion than normal resting platelets, and inherited the engulfed particles from parent MKs to assist in extrapulmonary particle transportation. Our findings collectively highlight that the specific responses of MKs towards inhaled particles and their roles in facilitating the translocation of particles from the lungs to extrapulmonary organs for clearance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2022042/Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS)
- 22076210/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 22150006/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

