Integrating cat boost algorithm with triangulating feature importance to predict survival outcome in recurrent cervical cancer
- PMID: 39191808
- PMCID: PMC11349876
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-67562-0
Integrating cat boost algorithm with triangulating feature importance to predict survival outcome in recurrent cervical cancer
Abstract
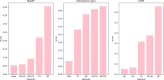
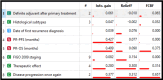
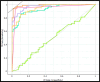
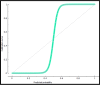
Cervical cancer is one of the most dangerous malignancies in women. Prolonged survival times are made possible by breakthroughs in early recognition and efficient treatment of a disease.The existing methods are lagging on finding the important attributes to predict the survival outcome. The main objective of this study is to find individuals with cervical cancer who are at greater risk of death from recurrence by predicting the survival.A novel approach in a proposed technique is Triangulating feature importance to find the important risk factors through which the treatment may vary to improve the survival outcome.Five algorithms Support vector machine, Naive Bayes, supervised logistic regression, decision tree algorithm, Gradient boosting, and random forest are used to build the concept. Conventional attribute selection methods like information gain (IG), FCBF, and ReliefFare employed. The recommended classifier is evaluated for Precision, Recall, F1, Mathews Correlation Coefficient (MCC), Classification Accuracy (CA), and Area under curve (AUC) using various methods. Gradient boosting algorithm (CAT BOOST) attains the highest accuracy value of 0.99 to predict survival outcome of recurrence cervical cancer patients. The proposed outcome of the research is to identify the important risk factors through which the survival outcome of the patients improved.
Keywords: Attribute selection; Cervival cancer; Gradient boosting; Recurrence; ReliefF.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Comparison of supervised machine learning classification techniques in prediction of locoregional recurrences in early oral tongue cancer.Int J Med Inform. 2020 Apr;136:104068. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.104068. Epub 2019 Dec 28. Int J Med Inform. 2020. PMID: 31923822
-
Bidirectional recurrent neural network approach for predicting cervical cancer recurrence and survival.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31641. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80472-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738223 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer prediction with transcriptome profiling using feature selection and machine learning methods.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Oct 1;23(1):410. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04965-8. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36183055 Free PMC article.
-
Can Predictive Modeling Tools Identify Patients at High Risk of Prolonged Opioid Use After ACL Reconstruction?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020 Jul;478(7):0-1618. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001251. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020. PMID: 32282466 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical cancer survival prediction by machine learning algorithms: a systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2023 Apr 13;23(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10808-3. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37055741 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From motion to meaning: understanding students' seating preferences in libraries through PIR-enabled machine learning and explainable AI.Front Psychol. 2025 Jul 11;16:1642381. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1642381. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40761460 Free PMC article.
-
A machine learning model for predicting severe mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in school-aged children.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Apr 21;25(1):570. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10958-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40259232 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geeitha, S. & Thangamani, M. A cognizant study of machine learning in predicting cervical cancer at various levels-a data mining concept. Int. J. Emerg. Technol.11(1), 23–28 (2020).
-
- Geeitha, S. & Thangamani, M. A Hybrid Model for Mining and Classification of Gene Expression Pattern for Detecting Neurodegenerative Disorder. In Progress in Advanced Computing and Intelligent Engineering (Springer, 2019).
-
- Alam, T. M., Khan, M. M. A., Iqbal, M. A., Wahab, A. & Mushtaq, M. Cervical cancer prediction through different screening methods using data mining. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl.10(2), 9 (2019).
-
- Ghoneim, A., Muhammad, G. & Hossain, M. S. Cervical cancer classification using convolutional neural networks and extreme learning machines. Future Gener. Comput. Syst.102, 643–649 (2020).10.1016/j.future.2019.09.015 - DOI

