Third-generation anti-CD19 CAR T cells for relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a phase 1/2 study
- PMID: 39192036
- PMCID: PMC11519001
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-024-02392-7
Third-generation anti-CD19 CAR T cells for relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a phase 1/2 study
Abstract
Third-generation chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CARTs) for relapsed or refractory (r/r) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) may improve efficacy compared to second-generation CARTs due to their enhanced CAR design. We performed the first phase 1/2 investigator-initiated trial evaluating escalating doses of third-generation CARTs (HD-CAR-1) targeting CD19 in patients with r/r CLL and B-cell lymphoma. CLL eligibility criteria were failure to two therapy lines including at least one pathway inhibitor and/or allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Nine heavily pretreated patients received HD-CAR-1 at dose levels ranging from 1 × 106 to 200 × 106 CART/m2. In-house HD-CAR-1 manufacturing was successful for all patients. While neurotoxicity was absent, one case of grade 3 cytokine release syndrome was observed. By day 90, six patients (67%) attained a CR, five of these (83%) with undetectable MRD. With a median follow-up of 27 months, 2-year PFS and OS were 30% and 69%, respectively. HD-CAR-1 products of responders contained significantly more CD4 + T cells compared to non-responders. In non-responders, a strong enrichment of effector memory-like CD8 + T cells with high expression of CD39 and/or CD197 was observed. HD-CAR-1 demonstrated encouraging efficacy and exceptionally low treatment-specific toxicity, presenting new treatment options for patients with r/r CLL. Trial registration: #NCT03676504.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AS: Travel grants from Hexal and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. Research grant from Therakos/Mallinckrodt. Consultancy BMS, Janssen‐Cilag. Co‐founder and part‐time employee of TolerogenixX LtD. of TolerogenixX Ltd. CMT: research support from Bayer AG. Advisory board member Pfizer, Janssen‐Cilag GmbH. Grants and/or provision of investigational medicinal products from Pfizer, Daiichi Sankyo, BiolineRx. MB: consulting fees from Amgen, research funding from Amgen, honoraria/ travel grants from Jazz, Celgene, Novartis, Pfizer and Amgen, advisory board member for Incyte, Amgen and AstraZeneca. MLS: consultancy for Kite/Gilead, Takeda. MS: research grants from Apogenix, Hexal and Novartis. Travel grants from Hexal and Kite. Financial support for educational activities and conferences from bluebird bio, Kite and Novartis. Advisory board member of MSD. (Co‐)PI of clinical trials of MSD, GSK, Kite and BMS. Co‐Founder and shareholder of TolerogenixX Ltd. PDe: honorarium from MSD. PDr: consultancy AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, Riemser, Roche; speakers bureau AbbVie, Gilead, Novartis, Riemser, Roche; research support from Neovii and Riemser. None of the mentioned sources supported the work described within this manuscript. ADH, AHK, AL, BM, BN, CR, FK, GK, HB, MR, SH, SY: none.
Figures

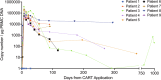
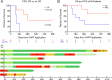
 : CART therapy;
: CART therapy;  : progressive disease;
: progressive disease;  : stable disease;
: stable disease;  : partial remission;
: partial remission;  : MRD-positive CR;
: MRD-positive CR;  : MRD-negative CR;
: MRD-negative CR;  : death;
: death;  : 2nd allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation;
: 2nd allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation;  : radiation therapy; A acalabrutinib, P pirtobrutinib, V venetoclax, Z zanubrutinib.
: radiation therapy; A acalabrutinib, P pirtobrutinib, V venetoclax, Z zanubrutinib.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

