Photodegradation of the phenylpyrazole insecticide ethiprole in aquatic environments and a comparison with fipronil
- PMID: 39192149
- PMCID: PMC11379744
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-024-34767-9
Photodegradation of the phenylpyrazole insecticide ethiprole in aquatic environments and a comparison with fipronil
Abstract
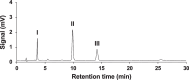
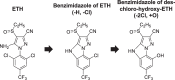
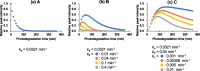
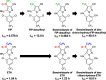
Ethiprole (ETH) is a phenylpyrazole insecticide that is used worldwide as an alternative to fipronil (FIP). Research on the photodegradation of ETH in aquatic environments has been limited compared with that on FIP. In this study, to clarify the photodegradation of ETH in aquatic systems, the photodegradation pathway and products were investigated using liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. We also determined the photochemical half-lives (t1/2) of ETH and its main degradation products. The primary photodegradation pathway was cyclization/dechlorination and hydroxylation/dechlorination of ETH to form the didechlorinated products (benzimidazole of des-chloro-hydroxy-ETH). Some newly identified photodegradation products and analogs of FIP photodegradation products were also detected as minor products. We compared the photodegradation of ETH with that of FIP under the same conditions. Didechlorinated products of ETH and FIP had the highest photostability. However, although the photochemical t1/2 of EHT was 2.7 times that of FIP, the photochemical t1/2 of the didechlorinated product of ETH was approximately one-third that of the didechlorinated product of FIP. This comparison of the photochemical processes of ETH and FIP provides new insight into the persistence and characteristics of both insecticides in the environment.
Keywords: High-resolution mass spectrometry; LC–MS/MS; Pesticide; Photo-dechlorination products; Photostability.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bobé A, Meallier P, Cooper JF, Coste CM (1998) Kinetics and mechanisms of abiotic degradation of fipronil (hydrolysis and photolysis). J Agric Food Chem 46:2834–2839. 10.1021/jf970874d 10.1021/jf970874d - DOI
-
- Caboni P, Sammelson RE, Casida JE (2003) Phenylpyrazole insecticide photochemistry, metabolism, and GABAergic action: ethiprole compared with fipronil. J Agric Food Chem 51:7055–7061. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jf030439l - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

