Recurrent myocardial infarction in a patient with median arcuate ligament syndrome: a case report and literature review
- PMID: 39192603
- PMCID: PMC11350549
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605241271891
Recurrent myocardial infarction in a patient with median arcuate ligament syndrome: a case report and literature review
Abstract
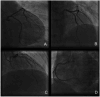
Median arcuate ligament (MAL) syndrome, otherwise known as celiac artery compression syndrome, is rare and is characterized by celiac artery compression by the median arcuate ligament. We report a unique case of MAL syndrome with recurrent myocardial infarction as the primary manifestation, and offer new pathophysiological insights. A man in his early 50s experienced recurrent upper abdominal pain, electrocardiographic changes, and elevated troponin concentrations, which suggested myocardial infarction. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography showed considerable celiac artery stenosis due to MAL syndrome. The patient was diagnosed with MAL syndrome and acute myocardial infarction. He declined revascularization owing to economic constraints, and opted to have conservative treatment with Chinese herbal extracts and medications. He succumbed to sudden cardiac death during a subsequent abdominal pain episode. The findings from this case show that MAL syndrome can present with recurrent myocardial infarction rather than typical intestinal angina symptoms. The pathophysiological link may involve intestinal and cardiac ischemia. An accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of MAL syndrome require careful evaluation and investigation.
Keywords: Myocardial infarction; abdominal pain; case report; celiac artery; median arcuate ligament syndrome; troponin.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Median arcuate ligament syndrome in an old male: a case report with occlusion of celiac artery after stenting.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 Apr 18;20(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s13019-025-03415-9. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 40251574 Free PMC article.
-
Hemodynamic benefits of celiac artery release for ruptured right gastric artery aneurysm associated with median arcuate ligament syndrome: a case report.BMC Surg. 2017 Nov 28;17(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12893-017-0320-0. BMC Surg. 2017. PMID: 29183305 Free PMC article.
-
Median Arcuate Ligament Syndrome - Literature Review and Case Report.Rev Port Cir Cardiotorac Vasc. 2017 Jul-Dec;24(3-4):111. Rev Port Cir Cardiotorac Vasc. 2017. PMID: 29701344 Review.
-
Ruptured Pancreaticoduodenal Artery Aneurysms Associated with Celiac Stenosis Caused by the Median Arcuate Ligament: A Poorly Known Etiology of Acute Abdominal Pain.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016 Feb;51(2):295-301. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2015.10.025. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2016. PMID: 26680452
-
Surgical treatment of median arcuate ligament syndrome: case report and review of literature.Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2015 Jan-Feb;143(1-2):74-8. doi: 10.2298/sarh1502074k. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2015. PMID: 25845256 Review.
References
-
- Gagnier JJ, Kienle G, Altman DG, CARE Group et al.. The CARE guidelines: consensus-based clinical case reporting guideline development. Headache 2013; 53: 1541–1547. - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, et al.; Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2018; 138: e618–e651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

