Asymmetric scapuloperoneal phenotype of MATR3-related distal myopathy: case series
- PMID: 39192891
- PMCID: PMC11347416
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1414928
Asymmetric scapuloperoneal phenotype of MATR3-related distal myopathy: case series
Abstract
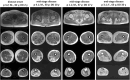
Recent research has sparked a discussion on the spectrum of diseases linked to the MATR3 gene associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and distal myopathy with vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness (VCPDM). To date, fewer than 50 cases of VCPDM have been reported in the literature. We aim to build upon the work of previous researchers by gathering additional information about VCPDM. In this study, we present six patients from four unrelated families affected by VCPDM. Our observations include patients exhibiting both the typical phenotype associated with MATR3-related distal myopathy and rare symptomatic manifestations of the disease. Notably, two cases presented with an asymmetric scapuloperoneal phenotype, leading in one case to an initial misdiagnosis of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy.
Keywords: ALS; FSHD; MATR3; distal myopathy; phenotypic variability; scapuloperoneal phenotype.
Copyright © 2024 Murtazina, Subbotin, Kuchina, Gilvanova, Degterev, Shchagina, Cherevatova, Bulakh, Sherstyukova, Ryzhkova, Kurushina, Skoblov, Borovikov and Kutsev.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cavalli M., Cardani R., Renna L. V., Toffetti M., Villa L., Meola G. (2021). First family of MATR3-related distal myopathy from Italy: the role of muscle biopsy in the diagnosis and characterization of a still poorly understood disease. Front. Neurol. 12, 715386. 10.3389/fneur.2021.715386 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feit H., Silbergleit A., Schneider L. B., Gutierrez J. A., Fitoussi R. P., Réyès C., et al. (1998). Vocal cord and pharyngeal weakness with autosomal dominant distal myopathy: clinical description and gene localization to 5q31. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63 (6), 1732–1742. 10.1086/302166 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

