PRONTO-TK: a user-friendly PROtein Neural neTwOrk tool-kit for accessible protein function prediction
- PMID: 39193069
- PMCID: PMC11348006
- DOI: 10.1093/nargab/lqae112
PRONTO-TK: a user-friendly PROtein Neural neTwOrk tool-kit for accessible protein function prediction
Abstract
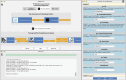
Associating one or more Gene Ontology (GO) terms to a protein means making a statement about a particular functional characteristic of the protein. This association provides scientists with a snapshot of the biological context of the protein activity. This paper introduces PRONTO-TK, a Python-based software toolkit designed to democratize access to Neural-Network based complex protein function prediction workflows. PRONTO-TK is a user-friendly graphical interface (GUI) for empowering researchers, even those with minimal programming experience, to leverage state-of-the-art Deep Learning architectures for protein function annotation using GO terms. We demonstrate PRONTO-TK's effectiveness on a running example, by showing how its intuitive configuration allows it to easily generate complex analyses while avoiding the complexities of building such a pipeline from scratch.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics.
Figures

References
-
- Rebecca K French and Edward C Holmes An Ecosystems perspective on virus evolution and emergence. Trends Microbiol. 2020; 28:165–175. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

