Advancements in MAX phase materials: structure, properties, and novel applications
- PMID: 39193282
- PMCID: PMC11348849
- DOI: 10.1039/d4ra03714f
Advancements in MAX phase materials: structure, properties, and novel applications
Abstract
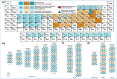
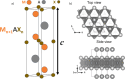
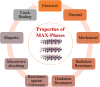
The MAX phase represents a diverse class of nanolaminate materials with intriguing properties that have received incredible global research attention because they bridge the divide separating metals and ceramics. Despite the numerous potential applications of MAX phases, their complex structure leads to a scarcity of readily accessible pure MAX phases. As a result, in-depth research on synthesis methods, characteristics, and structure is frequently needed for appropriate application. This review provides a comprehensive understanding of the recent advancements and growth in MAX phases, focusing on their complex crystal structures, unique mechanical, thermal, electrical, crack healing, corrosion-resistant properties, as well as their synthesis methods and applications. The structure of MAX phases including single metal MAX, i-MAX and o-MAX was discussed. Moreover, recent advancements in understanding MAX phase behaviour under extreme conditions and their potential novel applications across various fields, including high-temperature coatings, energy storage, and electrical and thermal conductors, biomedical, nanocomposites, etc. were discussed. Moreover, the synthesis techniques, ranging from bottom-up to top-down methods are scrutinized for their efficacy in tailoring MAX phase properties. Furthermore, the review explores the challenges and opportunities associated with optimizing MAX phase materials for specific applications, such as enhancing their oxidation resistance, tuning their mechanical properties, and exploring their functionality in emerging technologies. Overall, this review aims to provide researchers and engineers with a comprehensive understanding of MAX phase materials and inspire further exploration into their versatile applications in materials science and engineering.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




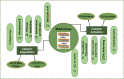
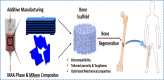
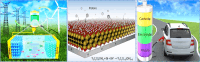

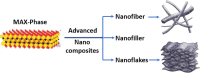
References
-
- Venkateshalu S. Grace A. N. MXenes—A new class of 2D layered materials: Synthesis, properties, applications as supercapacitor electrode and beyond. Appl. Mater. Today. 2020;18:100509.
-
- Zhao C. Zhang Y. Nie K. Yi L. Li B. Yuan Y. Liu Z. Recent advances in design and engineering of MXene-based heterostructures for sustainable energy conversion. Appl. Mater. Today. 2023;32:101841.
-
- Aleksanyan A. G. Dolukhanyan S. K. Mayilyan D. G. Muradyan G. N. Ter-Galstyan O. P. Mnatsakanyan N. L. Formation of Ti2AlNx MAX phase by “Hydride Cycle” and SHS methods. Ceram. Int. 2023;49:24229–24234.
-
- Alam S. Chowdhury M. A. Shahid A. Alam R. Rahim A. Synthesis of emerging two-dimensional (2D) materials–Advances, challenges and prospects. FlatChem. 2021;30:100305.
-
- Barsoum M. W. The MN+1AXN phases: A new class of solids: Thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2000;28:201–281.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

