Dynamic Landscape of Mpox Importation Risks Driven by Heavy-Tailed Sexual Contact Networks Among Men Who Have Sex With Men in 2022
- PMID: 39193849
- PMCID: PMC11793044
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiae433
Dynamic Landscape of Mpox Importation Risks Driven by Heavy-Tailed Sexual Contact Networks Among Men Who Have Sex With Men in 2022
Abstract
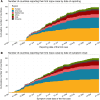
Background: During the 2022 global mpox outbreak, the cumulative number of countries reporting their first imported case quickly rose in the early phase, but the importation rate subsequently slowed down, leaving many countries reporting no cases by the 2022 year-end.
Methods: We developed a mathematical model of international dissemination of mpox infections incorporating sexual networks and global mobility data. We used this model to characterize the mpox importation patterns observed in 2022 and to discuss the potential of further international spread.
Results: Our proposed model better explained the observed importation patterns than models not assuming heterogeneity in sexual contacts. Estimated importation hazards decreased in most countries, surpassing the global case count decline, suggesting a reduced per-case risk of importation. We assessed each country's potential to export mpox cases until the end of an epidemic, identifying countries capable of contributing to the future international spread.
Conclusions: The accumulation of immunity among high-risk individuals over highly heterogeneous sexual networks may have contributed to the slowdown in the rate of mpox importations. Nevertheless, the existence of countries with the potential to contribute to the global spread of mpox highlights the importance of equitable resource access to prevent the global resurgence of mpox.
Keywords: depletion of susceptible; global spread; importation risk; mpox; sexual contact networks.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. F. M. has received a grant from AdvanSentinel Inc on the project of wastewater monitoring. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures



References
-
- Jezek Z, Grab B, Paluku KM, Szczeniowski MV. Human monkeypox: disease pattern, incidence and attack rates in a rural area of northern Zaire. Trop Geogr Med 1988; 40:73–83. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. 2022–23 mpox outbreak: global trends. 2023. https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/mpx_global/. Accessed 19 April 2023.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Fusion of Science and Technology and Japan Science and Technology Agency
- 20J00793/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- 200-2016-91781/SHEPheRD) program
- 101095619/ESCAPE
- A-0009841/National University of Singapore
- Joint Usage/Research Center Leading Academia in Marine and Environment Pollution Research
- European Union's Horizon 2023 research and innovation program
- 22K17329/JSPS Overseas Research Fellowships
- JP223fa627004/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 210758/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- JPMJPR22R3/Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology
- Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
- CC/CDC HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

