The Development of a Biomimetic Model of Bacteria Migration on Indwelling Urinary Catheter Surfaces
- PMID: 39194470
- PMCID: PMC11353059
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics9080491
The Development of a Biomimetic Model of Bacteria Migration on Indwelling Urinary Catheter Surfaces
Abstract
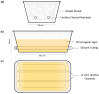
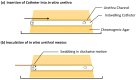
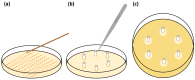
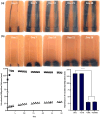
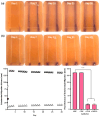
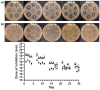
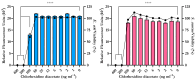
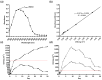
The aim of this study was to develop a novel biomimetic in vitro extraluminal migration model to observe the migration of bacteria along indwelling urinary catheters within the urethra and assess the efficacy of a prototype chlorhexidine diacetate (CHX) coating to prevent this migration. The in vitro urethra model utilised chromogenic agar. A catheter was inserted into each in vitro urethra. One side of the urethra was then inoculated with bacteria to replicate a contaminated urethral meatus. The models were then incubated for 30 days (d), with the migration distance recorded each day. Four indwelling catheter types were used to validate the in vitro urethra model and methodology. Using the biomimetic in vitro urethra model, E. coli and S. aureus migrated the entire length of a control catheter within 24-48 h (h). In the presence of a prototype CHX coating, full migration of the channel was prevented for 30 d. The results of this study support the hypothesis that catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) could be prevented by targeting catheter-mediated extraluminal microbial migration from outside of the urinary tract into the bladder.
Keywords: bacterial migration; biomimetic model; catheter-associated urinary tract infections; in vitro model; urethral catheterisation.
Conflict of interest statement
Joanne Fayne was employed by Teleflex® Medical EMEA throughout the duration of the study. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest. The results of this study have not been influenced by any personal or financial relationships with industry collaborators.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal J., Radera S. Biofilm-Mediated Urinary Tract Infections. In: Kumar S., Chandra N., Singh L., Hashmi M.Z., Varma A., editors. Biofilms in Human Diseases: Treatment and Control. 1st ed. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 177–214.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

