Microbead-Encapsulated Luminescent Bioreporter Screening of P. aeruginosa via Its Secreted Quorum-Sensing Molecules
- PMID: 39194612
- PMCID: PMC11352650
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14080383
Microbead-Encapsulated Luminescent Bioreporter Screening of P. aeruginosa via Its Secreted Quorum-Sensing Molecules
Abstract
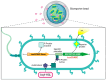
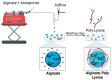
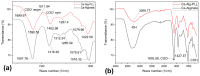
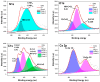
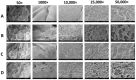
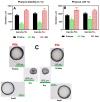
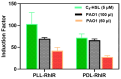
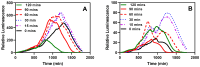
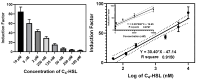
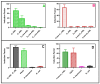
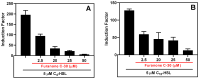
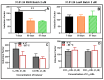
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic Gram-negative bacterium that remains a prevalent clinical and environmental challenge. Quorum-sensing (QS) molecules are effective biomarkers in pinpointing the presence of P. aeruginosa. This study aimed to develop a convenient-to-use, whole-cell biosensor using P. aeruginosa reporters individually encapsulated within alginate-poly-L-lysine (alginate-PLL) microbeads to specifically detect the presence of bacterial autoinducers. The PLL-reinforced microbeads were prepared using a two-step method involving ionic cross-linking and subsequent coating with thin layers of PLL. The alginate-PLL beads showed good stability in the presence of a known cation scavenger (sodium citrate), which typically limits the widespread applications of calcium alginate. In media containing synthetic autoinducers-such as N-(3-oxo dodecanoyl) homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL) and N-butanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL), or the cell-free supernatants of planktonic or the flow-cell biofilm effluent of wild P. aeruginosa (PAO1)-the encapsulated bacteria enabled a dose-dependent detection of the presence of these QS molecules. The prepared bioreporter beads remained stable during prolonged storage at 4 and -80 °C and were ready for on-the-spot sensing without the need for recovery. The proof-of-concept, optical fiber-based, and whole-cell biosensor developed here demonstrates the practicality of the encapsulated bioreporter for bacterial detection based on specific QS molecules.
Keywords: 3-oxo-C12-HSL; C4-HSL; Furanone C-30; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; QS inhibitor; alginate; autoinducers; bioencapsulation; hydrogels; microbeads; optical biosensors; poly-lysine; quorum sensing; whole-cell biosensors.
Conflict of interest statement
R.S.M. is the co-founder of footprints. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing molecule N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-l-homoserine lactone activates human platelets through intracellular calcium-mediated ROS generation.Int J Med Microbiol. 2018 Oct;308(7):858-864. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Int J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30098883
-
Encapsulation of Autoinducer Sensing Reporter Bacteria in Reinforced Alginate-Based Microbeads.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Jul 12;9(27):22321-22331. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b07166. Epub 2017 Jun 28. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017. PMID: 28627870 Free PMC article.
-
Autoinducer production and quorum-sensing dependent phenotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa vary according to isolation site during colonization of intubated patients.BMC Microbiol. 2007 Apr 18;7:33. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-33. BMC Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17442101 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging advances in biosensor technologies for quorum sensing signal molecules.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 Jan;417(1):33-50. doi: 10.1007/s00216-024-05659-1. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 39609273 Review.
-
[Advances in microbial whole-cell sensors for the detection of aromatic compounds].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2024 Sep 25;40(9):2899-2915. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.240137. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39319714 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Development of Covalently Functionalized Alginate-Pyrrole and Polypyrrole-Alginate Nanocomposites as 3D Printable Electroconductive Bioinks.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jul 1;18(13):3120. doi: 10.3390/ma18133120. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40649608 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Cell Fiber-Optic Biosensor for Real-Time, On-Site Sediment and Water Toxicity Assessment: Applications at Contaminated Sites Across Israel.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jun 22;15(7):404. doi: 10.3390/bios15070404. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kazemian H., Ghafourian S., Heidari H., Amiri P., Yamchi J.K., Shavalipour A., Houri H., Maleki A., Sadeghifard N. Antibacterial, anti-swarming and anti-biofilm formation activities of Chamaemelum nobile against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2015;48:432–436. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0065-2015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Winson M.K., Camara M., Latifi A., Foglino M., Chhabra S.R., Daykin M., Bally M., Chapon V., Salmond G., Bycroft B.W. Multiple N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone signal molecules regulate production of virulence determinants and secondary metabolites in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995;92:9427–9431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9427. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

