The Oral Administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis 557 (LDL557) Ameliorates the Progression of Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39194747
- PMCID: PMC11352892
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46080530
The Oral Administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis 557 (LDL557) Ameliorates the Progression of Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis
Abstract
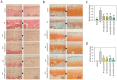
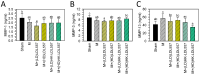
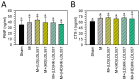
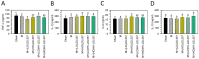
Low-grade body inflammation is a major cause of osteoarthritis (OA), a common joint disease. Gut dysbiosis may lead to systemic inflammation which can be prevented by probiotic administration. The Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis 557 (LDL557) has been demonstrated to have beneficial effects for anti-inflammation. This study investigated the effects of LDL557 on OA progress using monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-induced OA of rats. Live or heat-killed (HK)-LDL557 of a low or high dose was administrated for two weeks before MIA-induced OA, and then continuously administrated for another six weeks. After taking supplements for eight weeks, OA progress was analyzed. Results showed that MIA induced knee joint swelling, chondrocyte damage, and cartilage degradation, and supplementation with a high dose of LDL557 reduced MIA-induced knee joint swelling, chondrocyte damage, and cartilage degradation. Additionally, MIA increased serum levels of the matrix-degrading enzyme MMP-13, while a high dose of HK-LDL557 decreased it for the controls. Simultaneously, bone turnover markers and inflammatory cytokines of serum were assayed, but no significant differences were found except for a TNF-α decrease from a low dose of live LDL557. These results demonstrated that supplementation with high doses of live LDL557 or HK-LDL557 can reduce the progression of MIA-induced OA in rats.
Keywords: Lactobacillus delbrueckii; MMPs; inflammation; osteoarthritis; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors J.-S.L., H.-Y.H., and C.-C.L. are employed by SYNBIO TECH INC. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, the decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

