Therapeutic Effects of Semaglutide on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: An Open-Label Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39195185
- PMCID: PMC11354027
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases12080186
Therapeutic Effects of Semaglutide on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: An Open-Label Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been shown to improve glycemic control and insulin sensitivity and reduce body weight in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). This trial sought to evaluate the therapeutic effect of oral and subcutaneous semaglutide in NAFLD and its sequelae in obesity and/or T2D.
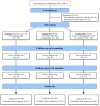
Methods: In an open-labelled intervention study, the sample was 180 patients classified into three parallel groups (1:1:1): group I received oral semaglutide, group II patients received injectable semaglutide, and group III received pioglitazone and/or vitamin E. Patients were evaluated at 6 and 12 months.
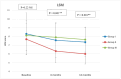
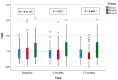
Results: There was a substantial improvement in lipid profile, liver enzymes, and body mass index, especially in group II. As for HDL, only group II showed a consistent increase at both 6 months (51 ± 4.62 mg/dL) and 12 months (50.08 ± 2.45 mg/dL) compared with baseline (45.6 ± 6.37 mg/dL) (p-value < 0.001). Despite the non-significant difference in NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) (p-value = 0.45 and 0.63), group II had significantly lower scores of the fibrosis-4 score (FIB-4), liver stiffness measurement (LSM), and controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) at 6 and 12 months (p-value < 0.001). Conclusions: Semaglutide improves lipid profile, liver steatosis, and fibrosis parameters and reduces the BMI in T2D and obese patients with NAFLD.
Keywords: GLP-1; clinical trial; diet study; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity; semaglutide; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

