Mechanism of Takifugu bimaculatus Skin Peptides in Alleviating Hyperglycemia in Rats with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus Based on Microbiome and Metabolome Analyses
- PMID: 39195493
- PMCID: PMC11355842
- DOI: 10.3390/md22080377
Mechanism of Takifugu bimaculatus Skin Peptides in Alleviating Hyperglycemia in Rats with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus Based on Microbiome and Metabolome Analyses
Abstract
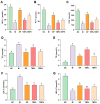
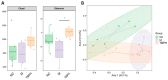
In this study, we aimed to explore the hypoglycemic effects of a hydrolysate on Takifugu bimaculatus skin (TBSH). The effect of the dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activities from different TBSH fractions was investigated on basic indexes, gut hormones, blood lipid indexes, viscera, and the gut microbiota and its metabolites in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The results showed that the <1 kDa peptide fraction from TBSH (TBP) exhibited a more potent DPP-IV inhibitory effect (IC50 = 0.45 ± 0.01 mg/mL). T2DM rats were induced with streptozocin, followed by the administration of TBP. The 200 mg/kg TBP mitigated weight loss, lowered fasting blood glucose levels, and increased insulin secretion by 20.47%, 25.23%, and 34.55%, respectively, rectified irregular hormonal fluctuations, lipid metabolism, and tissue injuries, and effectively remedied gut microbiota imbalance. In conclusion, TBP exerts a hypoglycemic effect in rats with T2DM. This study offers the potential to develop nutritional supplements to treat T2DM and further promote the high-value utilization of processing byproducts from T. bimaculatus. It will provide information for developing nutritional supplements to treat T2DM and further promote the high-value utilization of processing byproducts from T. bimaculatus.
Keywords: dipeptidyl peptidase-IV; gut microbiota; hypoglycemia; non-targeted metabolome; peptides of Takifugu bimaculatus skin; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Li L.-B., Zhong J.-X., Su J., Liu B. The research on the toxicity of parent fishes, fertilized eggs, embryo and juveniles of Fugu bimaculatus. J. Fish. Res. 2016;38:295.
-
- Go H.-J., Kim C.-H., Park J.B., Kim T.Y., Lee T.K., Oh H.Y., Park N.G. Biochemical and molecular identification of a novel hepcidin type 2-like antimicrobial peptide in the skin mucus of the pufferfish Takifugu pardalis. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019;93:683–693. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.08.017. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

