An engineered human cardiac tissue model reveals contributions of systemic lupus erythematosus autoantibodies to myocardial injury
- PMID: 39195859
- PMCID: PMC11399098
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-024-00525-w
An engineered human cardiac tissue model reveals contributions of systemic lupus erythematosus autoantibodies to myocardial injury
Abstract
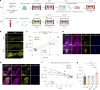
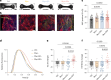
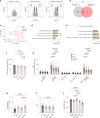
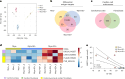
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a heterogenous autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs, including the heart. The mechanisms of myocardial injury in SLE remain poorly understood. In this study, we engineered human cardiac tissues and cultured them with IgG from patients with SLE, with and without myocardial involvement. IgG from patients with elevated myocardial inflammation exhibited increased binding to apoptotic cells within cardiac tissues subjected to stress, whereas IgG from patients with systolic dysfunction exhibited enhanced binding to the surface of live cardiomyocytes. Functional assays and RNA sequencing revealed that, in the absence of immune cells, IgG from patients with systolic dysfunction altered cellular composition, respiration and calcium handling. Phage immunoprecipitation sequencing (PhIP-seq) confirmed distinctive IgG profiles between patient subgroups. Coupling IgG profiling with cell surfaceome analysis identified four potential pathogenic autoantibodies that may directly affect the myocardium. Overall, these insights may improve patient risk stratification and inform the development of new therapeutic strategies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
An engineered human cardiac tissue model reveals contributions of systemic lupus erythematosus autoantibodies to myocardial injury.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 12:2024.03.07.583787. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.07.583787. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Sep;3(9):1123-1139. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00525-w. PMID: 38559188 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 3R01HL076485/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- 19TPA34910217/American Heart Association (American Heart Association, Inc.)
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB027062/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41EB027062/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
