ATF3 coordinates the survival and proliferation of cardiac macrophages and protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 39195894
- PMCID: PMC11358155
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-023-00392-x
ATF3 coordinates the survival and proliferation of cardiac macrophages and protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
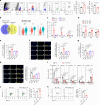
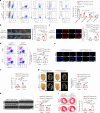
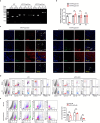
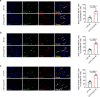
Cardiac resident MerTK+ macrophages exert multiple protective roles after ischemic injury; however, the mechanisms regulating their fate are not fully understood. In the present study, we show that the GAS6-inducible transcription factor, activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3), prevents apoptosis of MerTK+ macrophages after ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury by repressing the transcription of multiple genes involved in type I interferon expression (Ifih1 and Ifnb1) and apoptosis (Apaf1). Mice lacking ATF3 in cardiac macrophages or myeloid cells showed excessive loss of MerTK+ cardiac macrophages, poor angiogenesis and worse heart dysfunction after IR, which were rescued by the transfer of MerTK+ cardiac macrophages. GAS6 administration improved cardiac repair in an ATF3-dependent manner. Finally, we showed a negative association of GAS6 and ATF3 expression with the risk of major adverse cardiac events in patients with ischemic heart disease. These results indicate that the GAS6-ATF3 axis has a protective role against IR injury by regulating MerTK+ cardiac macrophage survival and/or proliferation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












Comment in
-
ATF3's shielding hand to counter ischemia-reperfusion injury in cardiac macrophages.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Jan;3(1):15-17. doi: 10.1038/s44161-023-00386-9. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 39195893 No abstract available.
References
-
- Horckmans, M. et al. Neutrophils orchestrate post-myocardial infarction healing by polarizing macrophages towards a reparative phenotype. Eur. Heart J.38, 187–197 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
