Effectiveness and safety of low dose Rituximab as remission-maintenance treatment for patients with refractory idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: results of a retrospective study from a monocentric cohort
- PMID: 39196499
- PMCID: PMC11442668
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-024-07079-z
Effectiveness and safety of low dose Rituximab as remission-maintenance treatment for patients with refractory idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: results of a retrospective study from a monocentric cohort
Abstract
Objective: Our aim was to assess efficacy and safety of Rituximab (RTX) in patients with refractory Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) from a monocentric cohort. Thereafter, we evaluated the efficacy of a low-dose RTX regimen as a remission-maintenance therapy.
Methods: We retrospectively evaluated a cohort of patients affected with IIM treated with RTX. All patients were refractory to glucocorticoids (GC) and at least one immunosuppressant. Two infusions of 1 g two weeks apart were considered as standard cycle of RTX, a single dose of 1 g every six months was deemed as a low-dose RTX regimen. Complete and partial response were defined according to physician's judgment, laboratory and radiological features.
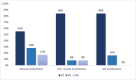
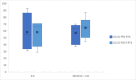
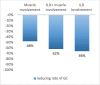
Results: Thirty-six patients affected with IIM were enrolled. Eighteen patients (50%) required the use of RTX for muscular involvement, 6 (16.7%) for interstitial lung disease (ILD), 12 (33.3%) for both myositis and ILD. We observed complete response to RTX in 25 patients (69.4%), partial response in 7 (19.4%) and no response in 4 (11.1%), with an overall response of 88.8% (partial and complete response). From the subgroup of twenty-five patients that achieved a complete response, six were treated with a low dose maintenance therapy maintaining a complete response to RTX. Twenty-six patients who achieved a complete or partial response were able to decrease the mean daily GC dose. Infections were the major adverse events detected in our study.
Conclusions: RTX shows favorable outcomes in refractory patients with IIM. A low-dose regimen of RTX appears to be effective in maintaining remission after induction with standard dose. Key Points • The precise pathogenic mechanism of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) remains elusive; however, a growing body of data support the autoimmune hypothesis. In this context, rituximab, a B cell-depleting agent, has emerged as a second-line therapeutic option in IIM. • Several studies have assessed It its effectiveness in refractory IIM patients. • Limited information exists on the use of Rituximab as maintenance therapy in patients who have achieved remission following induction therapy with Rituximab.
Keywords: Inflammatory myopathies; Interstitial lung disease; Maintenance treatment; Rituximab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Ghirardello A, Bettio S, Bassi N et al (2017) Autoantibody testing in patients with myositis: clinical accuracy of a multiparametric line immunoassay. Clin Exp Rheumatol 35:176–177 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

