Emerin deficiency drives MCF7 cells to an invasive phenotype
- PMID: 39198511
- PMCID: PMC11358522
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-70752-5
Emerin deficiency drives MCF7 cells to an invasive phenotype
Erratum in
-
Correction: Emerin deficiency drives MCF7 cells to an invasive phenotype.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 29;15(1):27632. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13048-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40730619 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
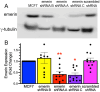
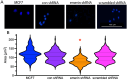
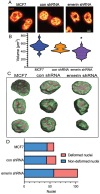
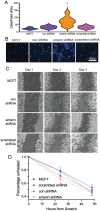
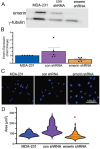
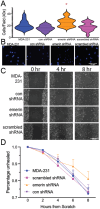
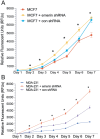
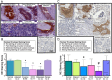
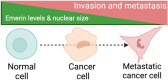
During metastasis, cancer cells traverse the vasculature by squeezing through very small gaps in the endothelium. Thus, nuclei in metastatic cancer cells must become more malleable to move through these gaps. Our lab showed invasive breast cancer cells have 50% less emerin protein resulting in smaller, misshapen nuclei, and higher metastasis rates than non-cancerous controls. Thus, emerin deficiency was predicted to cause increased nuclear compliance, cell migration, and metastasis. We tested this hypothesis by downregulating emerin in noninvasive MCF7 cells and found emerin knockdown causes smaller, dysmorphic nuclei, resulting in increased impeded cell migration. Emerin reduction in invasive breast cancer cells showed similar results. Supporting the clinical relevance of emerin reduction in cancer progression, our analysis of 192 breast cancer patient samples showed emerin expression inversely correlates with cancer invasiveness. We conclude emerin loss is an important driver of invasive transformation and has utility as a biomarker for tumor progression.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Emerin; Metastasis; Nucleoskeleton.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Emerin deficiency drives MCF7 cells to an invasive phenotype.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 7:2024.02.21.581379. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.21.581379. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;14(1):19998. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70752-5. PMID: 38712242 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of cancer: New dimensions. Cancer Discov.12(1), 31–46. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-1059 (2022). - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

