Predicting ground vibration during rock blasting using relevance vector machine improved with dual kernels and metaheuristic algorithms
- PMID: 39198596
- PMCID: PMC11358398
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-70939-w
Predicting ground vibration during rock blasting using relevance vector machine improved with dual kernels and metaheuristic algorithms
Abstract
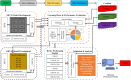
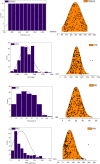
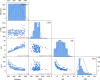
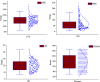
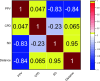
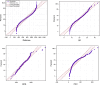
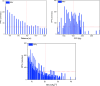
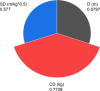
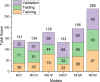
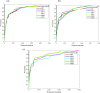
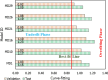
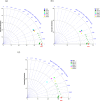
The ground vibration caused by rock blasting is an extremely hazardous outcome of the blasting operation. Blasting activity has detrimental effects on both the ecology and the human population living in proximity to the area. Evaluating the magnitude of blasting vibrations requires careful evaluation of the peak particle velocity (PPV) as a fundamental and essential parameter for quantifying vibration velocity. Therefore, this study employs models using the relevance vector machine (RVM) approach for predicting the PPV resulting from quarry blasting. This investigation utilized the conventional and optimized RVM models for the first time in ground vibration prediction. This work compares thirty-three RVM models to choose the most efficient performance model. The following conclusions have been mapped from the outcomes of the several analyses. The performance evaluation of each RVM model demonstrates each model achieved a performance of more than 0.85 during the testing phase, there was a strong correlation observed between the actual ground vibrations and the predicted ones. The analysis of performance metrics (RMSE = 21.2999 mm/s, 16.2272 mm/s, R = 0.9175, PI = 1.59, IOA = 0.8239, IOS = 0.2541), score analysis (= 93), REC curve (= 6.85E-03, close to the actual, i.e., 0), curve fitting (= 1.05 close to best fit, i.e., 1), AD test (= 11.607 close to the actual, i.e., 9.790), Wilcoxon test (= 95%), Uncertainty analysis (WCB = 0.0134), and computational cost (= 0.0180) demonstrate that PSO_DRVM model MD29 outperformed better than other RVM models in the testing phase. This study will help mining and civil engineers and blasting experts to select the best kernel function and its hyperparameters in estimating ground vibration during rock blasting project. In the context of the mining and civil industry, the application of this study offers significant potential for enhancing safety protocols and optimizing operational efficiency.
Keywords: Blasting; Genetic algorithm; Mining; PPV; Particle swarm optimization; Relevance vector machine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- B. O. Taiwo et al. Assessment of charge initiation techniques effect on blast fragmentation and environmental safety: An application of WipFrag software. 1–17 (2023).
-
- Taiwo, B. O. et al. Artificial neural network modeling as an approach to limestone blast production rate prediction: A comparison of PI-BANN and MVR models. J. Min. Environ.14(2), 375–388. 10.22044/jme.2023.12489.2266 (2023).10.22044/jme.2023.12489.2266 - DOI
-
- Y. Fissha, H. Ikeda, H. Toriya, N. Owada, T. Adachi, & Y. Kawamura. Evaluation and prediction of blast-induced ground vibrations: A Gaussian Process Regression (GPR) Approach. 659–682 (2023).
-
- Zhou, J., Li, C., Koopialipoor, M., Armaghani, D. J. & Pham, B. T. Development of a new methodology for estimating the amount of PPV in surface mines based on prediction and probabilistic models (GEP). Int. J. Mining Reclam. Environ.35(1), 48–68. 10.1080/17480930.2020.1734151 (2021).10.1080/17480930.2020.1734151 - DOI
-
- H. Zhang, J. Zhou, D. J. Armaghani, M. M. Tahir, & B. T. Pham. Applied sciences A combination of feature selection and random forest techniques to solve a problem related to. Appl. Sci. (2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

