Clonal hematopoiesis in LGI1-antibody encephalitis
- PMID: 39199016
- PMCID: PMC11514903
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.52192
Clonal hematopoiesis in LGI1-antibody encephalitis
Abstract
Objective: Leucine-rich glioma-inactivated 1 (LGI1)-antibody encephalitis (LGI1e), the major form of autoimmune encephalitis (AE) presented with memory loss and faciobrachial dystonic seizure, commonly develops in aged population. Hematologic aging is often accompanied by clonal hematopoiesis (CH), a phenomenon in which specific mutations accumulate, potentially leading to autoimmune disorders or malignancies. Our research aimed to investigate the connection between clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) and LGI1e.
Methods: Peripheral blood samples from consecutive LGI1e patients were collected and analyzed for 24 clonal CHIP using targeted gene sequencing. The results were compared to a control dataset from an ethnically matched health care cohort. Patient characteristics were analyzed based on their CHIP status.
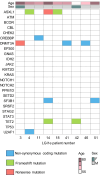
Results: A total of 52 LGI1e patients were enrolled for this study. Among them, three patients (5.8%) exhibited functional mutations in the ASXL1 gene, one of the CHIP-associated genes analyzed by targeted sequencing. This frequency was significantly higher compared to that of the control cohort (1%, p = 0.015). Nevertheless, the patients showed no difference in the clinical characteristics, laboratory results, and immunotherapy outcomes.
Interpretation: LGI1e showed high frequency of ASXL1 functional mutation in the CHIP analysis, which may contribute to the underlying pathogenesis. Further research is needed to determine its direct role in the development of autoimmunity and disease progression.
© 2024 The Author(s). Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no existing conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dalmau J, Graus F. Antibody‐mediated encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(9):840‐851. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

