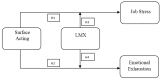
Exploring the Relationship between Surface Acting, Job Stress, and Emotional Exhaustion in Health Professionals: The Moderating Role of LMX
- PMID: 39199033
- PMCID: PMC11351417
- DOI: 10.3390/bs14080637
Exploring the Relationship between Surface Acting, Job Stress, and Emotional Exhaustion in Health Professionals: The Moderating Role of LMX
Abstract
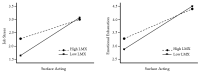
Rapid organizational changes due to technological advancements, high-efficiency expectations, and uncertainties, particularly in healthcare, have led to a global stress epidemic among em-ployees. This has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and evolving workplace practices. Surface acting, or the suppression and faking of emotions, significantly contributes to this stress and burnout, impacting not only individual healthcare professionals but also healthcare systems' overall effectiveness and sustainability. Providing adequate resources in high-demand work environments is, thus, essential to mitigate these negative experiences. Leader-member exchange (LMX) can play a pivotal role in understanding and addressing the needs and expectations of healthcare professionals. Drawing on Conservation of Resources (COR), Job Demands-Resources (JD-R), Social Exchange theories, and Grandey's Emotional Regulation Model, this study analyzed data from a convenience sample of 350 healthcare professionals. The results reveal that surface acting intensifies healthcare professionals' experiences of job stress and emotional exhaustion. Notably, the study empirically demonstrated that high levels of LMX in healthcare professionals' relationships with their leaders can mitigate the impact of surface acting on job stress and emotional exhaustion. These findings offer valuable insights for managers and policymakers, highlighting the importance of LMX in maintaining sustainable management practices in complex and stressful healthcare organizations.
Keywords: LMX; emotional exhaustion; health professionals; job stress; surface acting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Singh S., Chaturvedi S., Pasipanodya E.T. Handbook of Research on the Complexities and Strategies of Occupational Stress. IGI Global; Hershey, PA, USA: 2022. Antecedents and Outcomes of Occupational Stress: A Literature Review and Future Research Agenda; pp. 71–91.
-
- Lazarus R.S., Folkman S. Transactional theory and research on emotions and coping. Eur. J. Personal. 1987;1:141–169. doi: 10.1002/per.2410010304. - DOI
-
- Palmer S., Cooper C., Thomas K. A model of work stress. Couns. Work. 2004;5:25.
-
- Cooper C.L., Marshall J. Occupational sources of stress: A review of the literature relating to coronary heart disease and mental ill-health. J. Occup. Psychol. 1976;49:11–28. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8325.1976.tb00325.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources