The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Glutathione Synthesis in Individuals with Severe Obesity
- PMID: 39199212
- PMCID: PMC11351666
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13080967
The Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Glutathione Synthesis in Individuals with Severe Obesity
Abstract
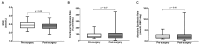
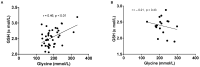
Glycine is deficient in individuals with obesity but improves following bariatric surgery. Glycine deficiency could impair glutathione (GSH) synthesis and worsen oxidative stress. We examined the impact of obesity-associated glycine deficiency and bariatric surgery on GSH synthesis. Twenty-one participants with severe obesity and twenty-one healthy weight controls were recruited. [1,2-13C2] glycine was infused to measure the erythrocyte (RBC) GSH synthesis rate. Participants with obesity underwent bariatric surgery, and 19 were restudied six months post-surgery. Compared to healthy weight controls, individuals with obesity had significantly lower concentrations of RBC GSH (2.43 ± 0.23 vs. 2.63 ± 0.26 mmol/L, p < 0.01). However, there were no differences in GSH fractional synthesis rate [78.0 (51.4-123.7) vs. 76.9 (49.3-110.1) % pool/day, p = 0.58] or absolute synthesis rate [1.85 (1.25-3.32) vs. 1.92 (1.43-3.03) mmol/L RBC/day, p = 0.97]. Despite a post-surgery increase in glycine concentration, no statistically significant changes in RBC GSH concentration or synthesis rates were detected. Further, the significant correlation between plasma glycine and RBC GSH concentration at baseline (r = 0.46, p < 0.01) was also lost following bariatric surgery. GSH concentration was significantly lower in participants with obesity, but bariatric surgery did not significantly increase GSH concentrations or synthesis rates.
Keywords: bariatric surgery; glutathione synthesis; glycine deficiency; severe obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glutathione synthesis is diminished in patients with uncontrolled diabetes and restored by dietary supplementation with cysteine and glycine.Diabetes Care. 2011 Jan;34(1):162-7. doi: 10.2337/dc10-1006. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Diabetes Care. 2011. PMID: 20929994 Free PMC article.
-
Erythrocyte glutathione deficiency in symptom-free HIV infection is associated with decreased synthesis rate.Am J Physiol. 1999 Jan;276(1):E205-11. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1999.276.1.E205. Am J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 9886968
-
Deficient synthesis of glutathione underlies oxidative stress in aging and can be corrected by dietary cysteine and glycine supplementation.Am J Clin Nutr. 2011 Sep;94(3):847-53. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.003483. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21795440 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Bariatric surgery in women of reproductive age: special concerns for pregnancy.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2008 Nov;(169):1-51. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2008. PMID: 20731480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutathione and glutathione-dependent enzymes: From biochemistry to gerontology and successful aging.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Dec;92:102066. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102066. Epub 2023 Sep 7. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 37683986 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-omics signature of healthy versus unhealthy lifestyles reveals associations with diseases.Hum Genomics. 2025 Aug 30;19(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s40246-025-00817-7. Hum Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40886004 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Alterations in Patients with Obesity and the Impact of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery: Insights for Future Research.Metabolites. 2025 Jun 26;15(7):434. doi: 10.3390/metabo15070434. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40710534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

