Quaternary Ammonium Salts-Based Materials: A Review on Environmental Toxicity, Anti-Fouling Mechanisms and Applications in Marine and Water Treatment Industries
- PMID: 39199346
- PMCID: PMC11352365
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14080957
Quaternary Ammonium Salts-Based Materials: A Review on Environmental Toxicity, Anti-Fouling Mechanisms and Applications in Marine and Water Treatment Industries
Abstract
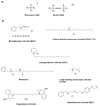
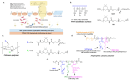
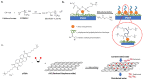
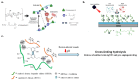
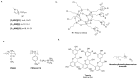
The adherence of pathogenic microorganisms to surfaces and their association to form antibiotic-resistant biofilms threatens public health and affects several industrial sectors with significant economic losses. For this reason, the medical, pharmaceutical and materials science communities are exploring more effective anti-fouling approaches. This review focuses on the anti-fouling properties, structure-activity relationships and environmental toxicity of quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) and, as a subclass, ionic liquid compounds. Greener alternatives such as QAS-based antimicrobial polymers with biocide release, non-fouling (i.e., PEG, zwitterions), fouling release (i.e., poly(dimethylsiloxanes), fluorocarbon) and contact killing properties are highlighted. We also report on dual-functional polymers and stimuli-responsive materials. Given the economic and environmental impacts of biofilms in submerged surfaces, we emphasize the importance of less explored QAS-based anti-fouling approaches in the marine industry and in developing efficient membranes for water treatment systems.
Keywords: anti-biofouling materials; environmental toxicity; ionic liquids (ILs); marine anti-fouling systems; quaternary ammonium salts (QASs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







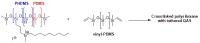



References
-
- Romani M., Warscheid T., Nicole L., Marcon L., Di Martino P., Suzuki M.T., Lebaron P., Lami R. Current and future chemical treatments to fight biodeterioration of outdoor building materials and associated biofilms: Moving away from ecotoxic and towards efficient, sustainable solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;802:149846. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149846. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Carvalho C.C.C.R. Marine Biofilms: A Successful Microbial Strategy with Economic Implications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018;5:126. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00126. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

