Extracellular Vesicles Induce Nuclear Factor-κB Activation and Interleukin-8 Synthesis through miRNA-191-5p Contributing to Inflammatory Processes: Potential Implications in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 39199417
- PMCID: PMC11352467
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14081030
Extracellular Vesicles Induce Nuclear Factor-κB Activation and Interleukin-8 Synthesis through miRNA-191-5p Contributing to Inflammatory Processes: Potential Implications in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
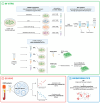
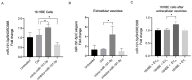
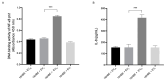
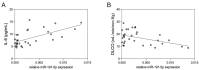
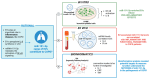
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a pivotal role in a variety of physiologically relevant processes, including lung inflammation. Recent attention has been directed toward EV-derived microRNAs (miRNAs), such as miR-191-5p, particularly in the context of inflammation. Here, we investigated the impact of miR-191-5p-enriched EVs on the activation of NF-κB and the expression of molecules associated with inflammation such as interleukin-8 (IL-8). To this aim, cells of bronchial epithelial origin, 16HBE, were transfected with miR-191-5p mimic and inhibitor and subsequently subjected to stimulations to generate EVs. Then, bronchial epithelial cells were exposed to the obtained EVs to evaluate the activation of NF-κB and IL-8 levels. Additionally, we conducted a preliminary investigation to analyze the expression profiles of miR-191-5p in EVs isolated from the plasma of patients diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Our initial findings revealed two significant observations. First, the exposure of bronchial epithelial cells to miR-191-5p-enriched EVs activated the NF-kB signaling and increased the synthesis of IL-8. Second, we discovered the presence of miR-191-5p in peripheral blood-derived EVs from COPD patients and noted a correlation between miR-191-5p levels and inflammatory and functional parameters. Collectively, these data corroborate and further expand the proinflammatory role of EVs, with a specific emphasis on miR-191-5p as a key cargo involved in this process. Consequently, we propose a model in which miR-191-5p, carried by EVs, plays a role in airway inflammation and may contribute to the pathogenesis of COPD.
Keywords: DLCO; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; extracellular vesicles; inflammation; interleukin-6; interleukin-8; microRNA-191; nuclear factor-κB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influenza-induced microRNA-155 expression is altered in extracellular vesicles derived from the COPD epithelium.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 May 27;15:1560700. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1560700. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40496017 Free PMC article.
-
SIV Infection Regulates Compartmentalization of Circulating Blood Plasma miRNAs within Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) and Extracellular Condensates (ECs) and Decreases EV-Associated miRNA-128.Viruses. 2023 Feb 24;15(3):622. doi: 10.3390/v15030622. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992331 Free PMC article.
-
miR-145-5p is associated with smoke-related chronic obstructive pulmonary disease via targeting KLF5.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Feb 25;300:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 30639269
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle microRNA: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Respiratory Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 23;25(17):9147. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179147. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of microarray data to identify potential signature genes and MiRNAs associated with the pathogenesis of asthma.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 15;23(1):796. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06646-5. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40665411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agustí A., Celli B.R., Criner G.J., Halpin D., Anzueto A., Barnes P., Bourbeau J., Han M.K., Martinez F.J., Montes de Oca M., et al. Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease 2023 Report: GOLD Executive Summary. Eur. Respir. J. 2023;61:2300239. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00239-2023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

