Therapeutic Senolysis of Axitinib-Induced Senescent Human Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 39199555
- PMCID: PMC11352446
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16162782
Therapeutic Senolysis of Axitinib-Induced Senescent Human Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) inhibit receptor-mediated signals in cells. Axitinib is a TKI with high specificity for vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs).
Aim: We determined whether axitinib could induce senescence in human cancer cells and be lysed by the senolytic drug ABT-263.
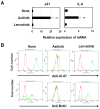
Methods: Human lung and breast adenocarcinoma cell lines were used. These cells were cultured with axitinib or a multi-target TKI lenvatinib. The expression of β-galactosidase, VEGFRs, Ki-67, reactive oxygen species (ROS) of cancer cells, and their BrdU uptake were evaluated by flow cytometry. The mRNA expression of p21 and IL-8 was examined by quantitative PCR. The effects of TKIs on phosphorylation of Akt and Erk1/2, as downstream molecules of VEGFR signaling, were examined by immunoblot. The in vivo anti-cancer effect was examined using a xenograft mice model.
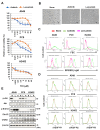
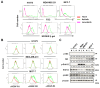
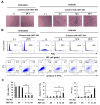
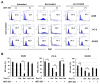
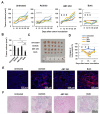
Results: Axitinib, but not lenvatinib, induced cellular senescence (increased cell size and enhanced expression of β-galactosidase) in all adenocarcinoma cell lines. Axitinib-induced senescence was unrelated to the expression of VEGFRs on cancer cells. ROS were involved in axitinib-induced senescence. Axitinib-induced senescent lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells were drastically lysed by ABT-263. In A549-xenografted mice, combination therapy with axitinib and ABT-263 significantly suppressed tumor growth with the induction of apoptotic cancer cells.
Keywords: axitinib; lung cancer; senescence; senolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Xie R., Wu J., Shang B., Bi X., Jiang W., Cao C., Zhou A., Shi H., Shou J. Optimizing targeted drug selection in combination therapy for patients with advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of safety. Cancer Med. 2023;12:7051–7064. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5504. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sonpavde G., Hutson T.E., Rini B.I. Axitinib for renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2008;17:741–748. - PubMed
-
- Motzer R.J., Robbins P.B., Powles T., Albiges L., Haanen J.B., Larkin J., Mu X.J., Ching K.A., Uemura M., Pal S.K., et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: Biomarker analysis of the phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial. Nat. Med. 2020;26:1733–1741. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1044-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

