Association between IGF-1 and IGFBPs in Blood and Follicular Fluid in Dairy Cows Under Field Conditions
- PMID: 39199904
- PMCID: PMC11350739
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14162370
Association between IGF-1 and IGFBPs in Blood and Follicular Fluid in Dairy Cows Under Field Conditions
Abstract
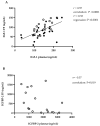
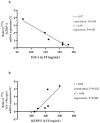
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) regulates dairy cow reproduction, while the paracrine IGF system locally influences fertility. In both systems, IGF-1 bioactivity is regulated through binding proteins (IGFBPs) inhibiting IGF-1 binding to its receptor (IGF1R). This study aimed to investigate a possible transfer between this endocrine and paracrine system. Therefore, blood and follicular fluid (FF) from postpartum dairy cows were analysed for ß-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), IGF-1, IGFBP-2, -3, -4, -5, and an IGFBP fragment in two study parts. The mRNA expression of IGFBP-2, IGFBP-4, IGF1R, and the pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) in granulosa cells was measured. The results showed correlations between plasma and FF for IGF-1 (r = 0.57, p < 0.001) and IGFBP-2 (r = -0.57, p < 0.05). Blood BHB negatively correlated with IGF-1 in blood and FF and IGFBP-3, -5 and total IGFBP in blood (IGF-1 plasma: r = -0.26, p < 0.05; FF: r = -0.35, p < 0.05; IGFBP-3: r = -0.64, p = 0.006; IGFBP-5: r = -0.49, p < 0.05; total IGFBP: r = -0.52, p < 0.05). A negative correlation was found between IGFBP-2 expression and IGF-1 concentration in FF (r = -0.97, p = 0.001), while an IGFBP fragment positively correlated with IGF1R-mRNA in FF (r = 0.82, p = 0.042). These findings suggest a transfer and local regulation between the somatotropic axis and the follicular IGF system, linking the metabolic status with local effects on dairy cow fertility.
Keywords: IGF-1; IGFBP; cattle; dairy cow; fertility; metabolic status; somatotropic axis.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. The author Christine Hoeflich has been working for the company Ligandis UG; Kirsten Mense, Ana Kassens and Hanna Grothmann are employed by SYNETICS Germany GmbH and Matthias Sommer is employed by Agrargenossenschaft Helmsdorf eG. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest..
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II), IGF-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), and IGFBP-4 in follicular fluid are associated with oocyte maturation and embryo development.Fertil Steril. 2006 Nov;86(5):1392-401. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2006.03.064. Fertil Steril. 2006. PMID: 17070193
-
Pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A and insulin-like growth factor binding protein mRNAs in granulosa cells of dominant and subordinate follicles of preovulatory cattle.Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2005 Jan;28(1):46-63. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2004.06.002. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15620806
-
Effect of negative energy balance on the insulin-like growth factor system in pre-recruitment ovarian follicles of post partum dairy cows.Reproduction. 2007 Mar;133(3):627-39. doi: 10.1530/REP-06-0122. Reproduction. 2007. PMID: 17379657
-
Functional differences in the growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor axis in cattle and pigs: implications for post-partum nutrition and reproduction.Reprod Domest Anim. 2008 Jul;43 Suppl 2:31-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2008.01140.x. Reprod Domest Anim. 2008. PMID: 18638098 Review.
-
Circulating and ovarian IGF binding proteins: potential roles in normo-ovulatory cycles and in polycystic ovarian syndrome.Prog Growth Factor Res. 1995;6(2-4):397-408. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(95)00016-x. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1995. PMID: 8817683 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

