Detection of Pharmaceutical Contamination in Amphipods of Lake Baikal by the HPLC-MS Method
- PMID: 39200038
- PMCID: PMC11350909
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13080738
Detection of Pharmaceutical Contamination in Amphipods of Lake Baikal by the HPLC-MS Method
Abstract
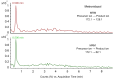
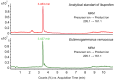
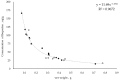
Pollution by active ingredients is one of the most significant and widespread forms of pollution on Earth. Medicines can have a negative impact on ecosystems, and contamination can have unpredictable consequences. An urgent and unexplored task is to study the Lake Baikal ecosystem and its organisms for the presence of trace concentrations of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Our study aimed to conduct a qualitative analysis of active pharmaceutical ingredients, and quantitative analysis of ibuprofen in endemic amphipods of Lake Baikal, using methods of high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS). Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), ibuprofen, acetaminophen, azithromycin, dimetridazole, metronidazole, amikacin, spiramycin, and some tetracycline antibiotics were detected in the studied littoral amphipods. We also detected different annual loads of active pharmaceutical ingredients on amphipods. Using the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode mentioned in GOST International Technical Standards, we detected molecules, fragmented as amikacin, chlortetracycline, doxycycline, oxytetracycline, dimetridazole, metronidazole and spiramycin. Thus, we first revealed that invertebrates of Lake Baikal can uptake pharmaceutical contaminants in the environment.
Keywords: Baikal; HPLC-MS; amphipods; antibiotics; endemics; ibuprofen; pharmaceutical pollution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic diversity of Microsporidia in the circulatory system of endemic amphipods from different locations and depths of ancient Lake Baikal.PeerJ. 2018 Aug 2;6:e5329. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5329. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 30083461 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a putatively multixenobiotic resistance related Abcb1 transporter in amphipod species endemic to the highly pristine Lake Baikal.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Apr;22(7):5453-68. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3758-y. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25367643
-
[Simultaneous determination of 40 plant growth regulators, fungicides, insecticides, and antibiotics in bean sprouts by QuEChERS-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry].Se Pu. 2022 Sep;40(9):843-853. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.12028. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 36156631 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Toxicity of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) acetylsalicylic acid, paracetamol, diclofenac, ibuprofen and naproxen towards freshwater invertebrates: A review.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Oct 20;740:140043. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140043. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32559537 Review.
-
Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:11-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23969330 Review.
References
-
- Bilal M., Mehmood S., Rasheed T., Iqbal H.M.N. Antibiotics Traces in the Aquatic Environment: Persistence and Adverse Environmental Impact. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2020;13:68–74. doi: 10.1016/j.coesh.2019.11.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

