Innovative Alignment-Based Method for Antiviral Peptide Prediction
- PMID: 39200068
- PMCID: PMC11350826
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13080768
Innovative Alignment-Based Method for Antiviral Peptide Prediction
Abstract
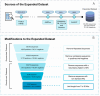
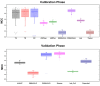
Antiviral peptides (AVPs) represent a promising strategy for addressing the global challenges of viral infections and their growing resistances to traditional drugs. Lab-based AVP discovery methods are resource-intensive, highlighting the need for efficient computational alternatives. In this study, we developed five non-trained but supervised multi-query similarity search models (MQSSMs) integrated into the StarPep toolbox. Rigorous testing and validation across diverse AVP datasets confirmed the models' robustness and reliability. The top-performing model, M13+, demonstrated impressive results, with an accuracy of 0.969 and a Matthew's correlation coefficient of 0.71. To assess their competitiveness, the top five models were benchmarked against 14 publicly available machine-learning and deep-learning AVP predictors. The MQSSMs outperformed these predictors, highlighting their efficiency in terms of resource demand and public accessibility. Another significant achievement of this study is the creation of the most comprehensive dataset of antiviral sequences to date. In general, these results suggest that MQSSMs are promissory tools to develop good alignment-based models that can be successfully applied in the screening of large datasets for new AVP discovery.
Keywords: StarPep toolbox; antiviral peptide; antiviral peptide dataset; machine learning; multi-query similarity search.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

