Rapid Phenotypic and Genotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Approaches for Use in the Clinical Laboratory
- PMID: 39200086
- PMCID: PMC11351821
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13080786
Rapid Phenotypic and Genotypic Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Approaches for Use in the Clinical Laboratory
Abstract
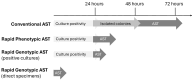
The rapid rise in increasingly resistant bacteria has become a major threat to public health. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) is crucial in guiding appropriate therapeutic decisions and infection prevention practices for patient care. However, conventional culture-based AST methods are time-consuming and labor-intensive. Therefore, rapid AST approaches exist to address the delayed gap in time to actionable results. There are two main types of rapid AST technologies- phenotypic and genotypic approaches. In this review, we provide a summary of all commercially available rapid AST platforms for use in clinical microbiology laboratories. We describe the technologies utilized, performance characteristics, acceptable specimen types, types of resistance detected, turnaround times, limitations, and clinical outcomes driven by these rapid tests. We also discuss crucial factors to consider for the implementation of rapid AST technologies in a clinical laboratory and what the future of rapid AST holds.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; diagnostics; infection prevention; molecular technologies; multiplex PCR; rapid antimicrobial susceptibility.
Conflict of interest statement
R.Y. reports research funding from Q-linea and serves on the working document groups for CLSI. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrer R., Martin-Loeches I., Phillips G., Osborn T.M., Townsend S., Dellinger R.P., Artigas A., Schorr C., Levy M.M. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: Results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit. Care Med. 2014;42:1749–1755. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000330. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous