Evaluation of Anti-CAR Linker mAbs for CAR T Monitoring after BiTEs/bsAbs and CAR T-Cell Pretreatment
- PMID: 39200107
- PMCID: PMC11351819
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12081641
Evaluation of Anti-CAR Linker mAbs for CAR T Monitoring after BiTEs/bsAbs and CAR T-Cell Pretreatment
Abstract
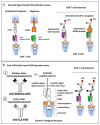
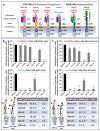
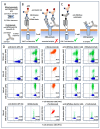
For the monitoring of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies, antigen-based CAR detection methods are usually applied. However, for each target-antigen, a separate detection system is required. Furthermore, when monitored CAR T-cells in the blood of patients treated with bispecific antibodies or T-cell engagers (bsAbs/BiTEs) recognize the same antigen, these methods produce false-positive results in clinical diagnostics. Anti-CAR-linker monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the linker sequence between the variable domains of the antigen binding CAR fragment promise a universal and unbiased CAR detection. To test this, we analyzed clinical specimens of all BCMA- and CD19-targeting CAR T-cell products currently approved for clinical use. We found a highly specific and sensitive CAR detection using anti-CAR-linker mAb in blood cells from patients treated with Ide-cel, Tisa-cel, Axi-cel, Brexu-cel, and Liso-cel. For Ide-cel and Tisa-cel, the sensitivity was significantly lower compared to that for antigen-based CAR detection assays. Strikingly, the specificity of anti-CAR linker mAb was not affected by the simultaneous presence of bispecific blinatumomab or teclistamab for Axi-cel, Brexu-cel, Liso-cel, or Ide-cel, respectively. Cilta-cel (containing a monomeric G4S-CAR linker) could not be detected by anti-CAR linker mAb. In conclusion, anti-CAR-linker mAbs are highly specific and useful for CAR T-cell monitoring but are not universally applicable.
Keywords: BiTE; CAR; CAR T-cell monitoring; anti-CAR-linker mAbs; bispecific antibody; combination treatments; detection; diagnostic.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors M.M., V.V. and U.P. were employed by the companies Janssen and BMS. Author U.K. was employed as consultant by the companies AstraZeneca, Affimed, Glycostem, GammaDelta, and Zelluna. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Westin J.R., Kersten M.J., Salles G., Abramson J.S., Schuster S.J., Locke F.L., Andreadis C. Efficacy and safety of CD19-directed CAR-T cell therapies in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas: Observations from the JULIET, ZUMA-1, and TRANSCEND trials. Am. J. Hematol. 2021;96:1295–1312. doi: 10.1002/ajh.26301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

