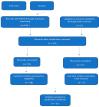
Disseminated Peritoneal Leiomyomatosis-A Challenging Diagnosis-Mimicking Malignancy Scoping Review of the Last 14 Years
- PMID: 39200214
- PMCID: PMC11351519
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12081749
Disseminated Peritoneal Leiomyomatosis-A Challenging Diagnosis-Mimicking Malignancy Scoping Review of the Last 14 Years
Abstract
Disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis (DPL) is a rare condition marked by multiple leiomyomas in the peritoneal cavity, predominantly affecting women of reproductive age. Although typically benign, DPL can present significant diagnostic challenges and, in rare cases, may progress to malignancy. A primary contributing factor to DPL is iatrogenic, particularly due to surgical interventions such as morcellation during myomectomy. This scoping review explores the pathogenesis, epidemiology, diagnosis, and management of DPL, highlighting the crucial role of hormonal influences and iatrogenic factors. Diagnostic methods include computed tomography, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging, and histopathological evaluation, which are essential for assessing disease extent and guiding treatment. Management strategies encompass surgical intervention-with a focus on minimizing iatrogenic risks-conservative approaches for asymptomatic patients, and advancements in hormonal treatments. Emphasis is placed on preventing iatrogenic dissemination through refined surgical techniques and patient education. Despite its rarity, with fewer than 200 cases reported globally, understanding DPL's clinical presentation and iatrogenic origins is vital for optimal patient outcomes. This review underscores the importance of early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and ongoing research to address the challenges associated with DPL.
Keywords: disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis; hormonal theory; myomectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rosati A., Vargiu V., Angelico G., Zannoni G.F., Ciccarone F., Scambia G., Fanfani F. Disseminated peritoneal leiomyomatosis and malignant transformation: A case series in a single referral center. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2021;262:21–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2021.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources