Cardiovascular and Renal Effects Induced by Alpha-Lipoic Acid Treatment in Two-Kidney-One-Clip Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 39200216
- PMCID: PMC11351279
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12081751
Cardiovascular and Renal Effects Induced by Alpha-Lipoic Acid Treatment in Two-Kidney-One-Clip Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
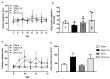
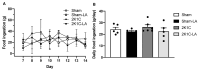
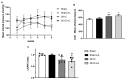
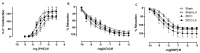
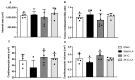
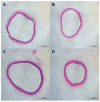
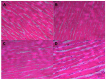
α-Lipoic acid (LA) is an antioxidant of endogenous production, also obtained exogenously. Oxidative stress is closely associated with hypertension, which causes kidney injury and endothelial dysfunction. Here, we evaluated the cardiovascular and renal effects of LA in the two-kidney-one-clip (2K1C) hypertension model. The rats were divided into four groups: Sham surgery (Sham), the two-kidneys-one-clip (2K1C) group, and groups treated with LA for 14 days (Sham-LA and 2K1C-LA). No changes were observed in the pattern of food, water intake, and urinary volume. The left/right kidney weight LKw/RKw ratio was significantly higher in 2K1C animals. LA treatment did not reverse the increase in cardiac mass. In relation to vascular reactivity, there was an increase in the potency of phenylephrine (PHE) curve in the hypertensive animals treated with LA compared to the 2K1C group and also compared to the Sham group. Vasorelaxation induced by acetylcholine (Ach) and sodium nitroprusside (SNP) were not improved by treatment with LA. Urea and creatinine levels were not altered by the LA treatment. In conclusion, the morphological changes in the aorta and heart were not reversed; however, the treatment with LA mitigated the contraction increase induced by the 2K1C hypertension.
Keywords: 2K1C; antioxidant; hypertension; lipoic acid; oxidative stress; renal function; renin–angiotensin system; vascular reactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
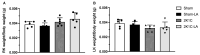
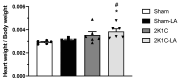
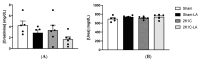
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

