Effects of L-Ornithine-L-Aspartate on Angiogenesis and Perfusion in Subacute Hind Limb Ischemia: Preliminary Study
- PMID: 39200251
- PMCID: PMC11351382
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12081787
Effects of L-Ornithine-L-Aspartate on Angiogenesis and Perfusion in Subacute Hind Limb Ischemia: Preliminary Study
Abstract
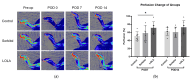
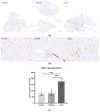
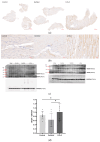
The current treatment options for peripheral arterial disease (PAD) are limited due to a lack of significant high-level evidence to inform clinical decisions and unfavorable outcomes in terms of cost-effectiveness and amputation rates. In order to suggest the use of the commercially available L-Ornithine-L-Aspartate (LOLA) for treating PAD, we induced hind limb ischemia (HLI) by unilaterally ligating the femoral artery in a rat model. The rats were randomly divided into three groups, with seven rats assigned to each group: group 1 (control), group 2 (sorbitol), and group 3 (LOLA). Intraperitoneal injections were administered five times on post-operative days (PODs) 3, 5, 7, 10, and 12. Perfusion imaging was conducted on PODs 7 and 14 and compared to pre-operative perfusion imaging. Immunohistochemistry staining and Western blotting were performed after the final perfusion imaging. Group 3 showed a significant increase in perfusion, high CD31-positive capillary lumen density, and substantial overexpression of VEGF in the ischemic limb during the subacute phase of HLI. In conclusion, this study provides the first documented evidence of angiogenesis and perfusion recovery in the subacute phase of the HLI model following the administration of LOLA. With LOLA readily available on the commercial market, the implementation of LOLA treatment for PAD in humans can be expedited compared to other therapies still in the developmental stage.
Keywords: L-ornithine-L-aspartate; angiogenesis; peripheral arterial disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene therapy with Pellino-1 improves perfusion and decreases tissue loss in Flk-1 heterozygous mice but fails in MAPKAP Kinase-2 knockout murine hind limb ischemia model.Microvasc Res. 2022 May;141:104311. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2022.104311. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Microvasc Res. 2022. PMID: 34999110 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a two-stage limb ischemia model to better simulate human peripheral artery disease.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 26;10(1):3449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60352-4. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32103073 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of Thioredoxin1 enhances functional recovery in a mouse model of hind limb ischemia.J Surg Res. 2017 Aug;216:158-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.04.019. Epub 2017 May 5. J Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28807201
-
[Physiological functions of L-ornithine and L-aspartate in the body and the efficacy of administration of L-ornithine-L-aspartate in conditions of relative deficiency].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2010 Jun;28(168):490-5. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2010. PMID: 20642112 Review. Polish.
-
Hepatoprotection by L-Ornithine L-Aspartate in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Dig Dis. 2019;37(1):63-68. doi: 10.1159/000491429. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Dig Dis. 2019. PMID: 30016770 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Criqui M.H., Matsushita K., Aboyans V., Hess C.N., Hicks C.W., Kwan T.W., McDermott M.M., Misra S., Ujueta F. Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: Contemporary Epidemiology, Management Gaps, and Future Directions: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;144:e171–e191. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

