Metabolic Changes Following Smoking Cessation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 39200346
- PMCID: PMC11352061
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12081882
Metabolic Changes Following Smoking Cessation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Background: Smoking cessation is crucial for reducing complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), but associated weight gain can worsen glycemic control, discouraging quitting attempts. Varenicline, a partial agonist of α4β2 nicotinic receptors, aids smoking cessation. This study examines the effects of varenicline on body weight and metabolic parameters in patients with T2DM and prediabetes.
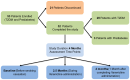
Methods: Fifty-three patients were enrolled, of which 32 successfully quit smoking after a three-month course of varenicline and were examined after an additional month with no medication. Measurements taken at baseline, 2.5 months, and 4 months included body weight, blood pressure, resting metabolic rate (RMR), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting glucose, blood lipids, C-reactive protein (CRP), appetite-related hormones, and physical activity.
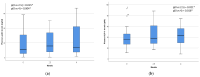
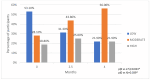
Results: Post-treatment, there were no significant changes in body weight, blood pressure, RMR, or glycemic control. Total (CHOL) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) cholesterol decreased significantly at 4 months of the study (from 168 to 156 mg/dL, p = 0.013, and from 96 to 83 mg/dL, p = 0.013, respectively). Leptin levels increased (from 11 to 13.8 ng/dL, p = 0.004), as did glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) levels (from 39.6 to 45.8 pM, p = 0.016) at 4 months of follow-up. The percentage of participants who reported moderate-intensity activity increased from 28% to 56%, while those reporting high-intensity activity increased from 19% to 22%, respectively (p = 0.039).
Conclusions: Our study showed that smoking cessation with varenicline in smokers with T2DM and prediabetes led to significant improvements in lipid profile, significant increase in plasma leptin and GLP-1 levels, and increased physical activity, without significant weight gain. Thus, smoking cessation without weight gain or deteriorated glycemic control is feasible for these smokers, with added benefits to lipid profiles, GLP-1 regulation, and physical activity.
Keywords: appetite-related hormones; diabetes; metabolic parameters; physical activity; smoking cessation; varenicline; weight gain.
Conflict of interest statement
Author A.K. is employed by the company AstraZeneca Greece. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The company AstraZeneca Greece had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of dulaglutide in promoting abstinence during smoking cessation: a single-centre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group trial.EClinicalMedicine. 2023 Feb 21;57:101865. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101865. eCollection 2023 Mar. EClinicalMedicine. 2023. PMID: 36874396 Free PMC article.
-
A double blind randomized controlled trial investigating efficacy and safety of varenicline for smoking cessation in patients with type 2 diabetes: study protocol.Intern Emerg Med. 2021 Oct;16(7):1823-1839. doi: 10.1007/s11739-021-02684-1. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Intern Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33735416 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Smoking cessation efficacy and safety of varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor partial agonist.J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2006 Nov-Dec;21(6):433-6. doi: 10.1097/00005082-200611000-00004. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2006. PMID: 17293731 Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of Smoking Cessation on Body Weight and Other Metabolic Parameters with Focus on People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 14;19(20):13222. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013222. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36293800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for waterpipe smoking cessation.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jun 7;6(6):CD005549. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005549.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37286509 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Associations of Serum GIP, GLP-1, and DPP-4 with Metabolic and Hormonal Profiles and Tobacco Exposure in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 23;26(15):7097. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157097. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806228 Free PMC article.
-
The nonlinear relationship between the ratio of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 19;12:1492483. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1492483. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40046913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peng K., Chen G., Liu C., Mu Y., Ye Z., Shi L., Zhao J., Chen L., Li Q., Yang T. Association between smoking and glycemic control in diabetic patients: R esults from the R isk E valuation of c A ncers in C hinese diabe T ic I ndividuals: A l ON gitudinal (REACTION) study. J. Diabetes. 2018;10:408–418. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12625. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

