Anti-Biofilm Effects of Z102-E of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum against Listeria monocytogenes and the Mechanism Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis
- PMID: 39200422
- PMCID: PMC11354177
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13162495
Anti-Biofilm Effects of Z102-E of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum against Listeria monocytogenes and the Mechanism Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis
Abstract
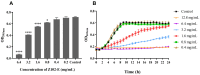
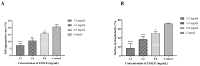
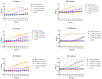
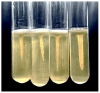
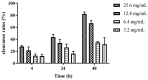
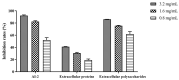
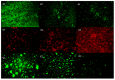
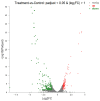
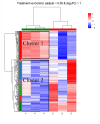
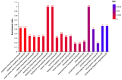
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are the most common probiotics, and they present excellent inhibitory effects on pathogenic bacteria. This study aimed to explore the anti-biofilm potential of the purified active substance of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, named Z102-E. The effects of Z102-E on Listeria monocytogenes were investigated in detail, and a transcriptomic analysis was conducted to reveal the anti-biofilm mechanism. The results indicated that the sub-MIC of Z102-E (3.2, 1.6, and 0.8 mg/mL) decreased the bacterial growth and effectively reduced the self-aggregation, surface hydrophobicity, sugar utilization, motility, biofilm formation, AI-2 signal molecule, contents of extracellular polysaccharides, and extracellular protein of L. monocytogenes. Moreover, the inverted fluorescence microscopy observation confirmed the anti-biofilm effect of Z102-E. The transcriptomic analysis indicated that 117 genes were up-regulated and 214 were down-regulated. Z102-E regulated the expressions of genes related to L. monocytogenes quorum sensing, biofilm formation, etc. These findings suggested that Z102-E has great application potential as a natural bacteriostatic agent.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum; Listeria monocytogenes; anti-biofilm; motility; quorum sensing; transcriptomic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibiofilm and Antiquorum Sensing Potential of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Z057 against Vibrio parahaemolyticus.Foods. 2022 Jul 27;11(15):2230. doi: 10.3390/foods11152230. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35892815 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes biofilm inhibition on food contact surfaces by application of postbiotics from Lactobacillus curvatus B.67 and Lactobacillus plantarum M.2.Food Res Int. 2021 Oct;148:110595. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110595. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34507740
-
Spent coffee ground disrupts Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation through inhibition of motility and adhesion via quorum sensing regulation.Int J Food Microbiol. 2025 Feb 16;430:111066. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2025.111066. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Int J Food Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39823805
-
Screening, probiotic properties, and inhibition mechanism of a Lactobacillus antagonistic to Listeria monocytogenes.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Jan 1;906:167587. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167587. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 37797767
-
Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum against Listeria monocytogenes isolated from milk, chicken and pregnant women.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 19;14:1201201. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1201201. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37538844 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of a TonB-Dependent Siderophore Receptor as a Novel Anti-Biofilm Target and Virtual Screening for Its Inhibitor in Pseudomonas fluorescens PF08.Foods. 2025 Feb 6;14(3):531. doi: 10.3390/foods14030531. Foods. 2025. PMID: 39942124 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm effects of bacteriocin PCM7-4 on Listeria monocytogenes.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 5;20(6):e0325109. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325109. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40471979 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced biomaterials for targeting mature biofilms in periodontitis therapy.Bioact Mater. 2025 Feb 27;48:474-492. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.02.026. eCollection 2025 Jun. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40093304 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Osimani A., Clementi F. The occurrence of Listeria monocytogenes in mass catering: An overview in the European Union. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2016;57:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2016.05.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

