Metabolomic Approaches to Study the Potential Inhibitory Effects of Plantaricin Q7 against Listeria monocytogenes Biofilm
- PMID: 39200500
- PMCID: PMC11353926
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13162573
Metabolomic Approaches to Study the Potential Inhibitory Effects of Plantaricin Q7 against Listeria monocytogenes Biofilm
Abstract
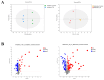
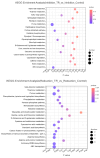
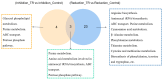
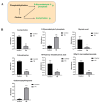
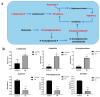
Listeria monocytogenes is a serious pathogen and can exacerbate harmful effects through the formation of biofilm. Inhibition of or reduction in L. monocytogenes biofilm is a promising strategy to control L. monocytogenes in the food industry. In our previous study, it was found that plantaricin Q7 produced by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Q7 could inhibit and reduce L. monocytogenes biofilm, but the specific mechanism remains unclear. In this study, the inhibitive and reduced activity of plantaricin Q7 on L. monocytogenes biofilm was investigated by metabolomics. The results showed that plantaricin Q7 inhibited the synthesis of L. monocytogenes biofilm mainly through purine metabolism and glycerol phospholipid metabolism, and the key differential metabolites included acetylcholine and hypoxanthine with a decrease in abundance from 5.80 to 4.85. In addition, plantaricin Q7 reduced the formed L. monocytogenes biofilm by purine metabolism and arginine biosynthesis, and the main differential metabolites were N-acetylglutamate and D-ribose-1-phosphate with a decrease in abundance from 6.21 to 4.73. It was the first report that purine metabolism and amino acid metabolism were the common metabolic pathway for plantaricin Q7 to inhibit and reduce L. monocytogenes biofilm, which could be potential targets to control L. monocytogenes biofilm. A putative metabolic pathway for L. monocytogenes biofilm inhibition and reduction by plantaricin Q7 was proposed. These findings provided a novel strategy to control L. monocytogenes biofilm in food processing.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes biofilm; inhibition; metabolomics; plantaricin Q7; reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative Metabolomics Analyses of Plantaricin Q7 Production by Lactobacillus plantarum Q7.J Agric Food Chem. 2021 Sep 15;69(36):10741-10748. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03533. Epub 2021 Sep 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 34478301
-
Adsorption of plantaricin Q7 on montmorillonite and application in feedback regulation of plantaricin Q7 synthesis by Lactobacillus plantarum Q7.Eng Life Sci. 2018 Nov 15;19(1):57-65. doi: 10.1002/elsc.201800086. eCollection 2019 Jan. Eng Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 32624956 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Fructose and Overexpression of Shock-Related Gene groL on Plantaricin Q7 Production.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020 Mar;12(1):32-38. doi: 10.1007/s12602-019-09537-6. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020. PMID: 30887309
-
Structural and biosynthetic diversity of plantaricins from Lactiplantibacillus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Sep;107(18):5635-5649. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12692-0. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37493805 Review.
-
Recent advances on the formation, detection, resistance mechanism, and control technology of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm in food industry.Food Res Int. 2024 Mar;180:114067. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114067. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38395584 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Analysis of Listeria monocytogenes Subjected to Pulsed Magnetic Field.Foods. 2025 May 24;14(11):1871. doi: 10.3390/foods14111871. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abou E., Elsohaby I., Al-Mohammadi A., Seliem M., Tahoun A., Abousaty A., Algendy R.M., Mohamed E.A.A., El-Gazzar N. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum against Listeria monocytogenes isolated from milk, chicken and pregnant women. Front. Microbiol. 2023;14:1201201. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1201201. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee B.-H., Cole S., Badel-Berchoux S., Guillier L., Felix B., Krezdorn N., Hébraud M., Bernardi T., Sultan I., Piveteau P. Biofilm formation of Listeria monocytogenes strains under food processing environments and pan-genome-wide association study. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:2698. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02698. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

