Critical Review of Food Colloidal Delivery System for Bioactive Compounds: Physical Characterization and Application
- PMID: 39200523
- PMCID: PMC11353541
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13162596
Critical Review of Food Colloidal Delivery System for Bioactive Compounds: Physical Characterization and Application
Abstract
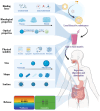
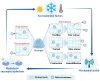
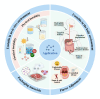
Bioactive compounds (BACs) have attracted much attention due to their potential health benefits. However, such substances have problems such as difficulty dissolving in water, poor stability, and low intestinal absorption, leading to serious limitations in practical applications. Nowadays, food colloidal delivery carriers have become a highly promising solution due to their safety, controllability, and efficiency. The use of natural macromolecules to construct delivery carriers can not only regulate the solubility, stability, and intestinal absorption of BACs but also effectively enhance the nutritional added value of functional foods, improve sensory properties, and extend shelf life. Moreover, smart-responsive colloidal delivery carriers can control the release characteristics of BACs, thus improving their absorption rate in the human body. This review describes the characteristics of several typical food colloid delivery carriers, focuses on their physical properties from static structure to dynamic release, summarizes their applications in delivery systems, and provides an outlook on the future development of food colloid delivery carriers. The different compositions and structures of food colloids tend to affect their stability and release behaviors, and the different surface properties and rheological characteristics of the carriers predestine their different application scenarios. The control of in vivo release properties and the effect on food media should be emphasized in the future exploration of safer and more controllable carrier systems.
Keywords: application; delivery system; food colloid; physical characteristic; structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein-Pectin Delivery Carriers for Food Bioactive Ingredients: Preparation, Release Mechanism, and Application.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025 May;24(3):e70183. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70183. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025. PMID: 40285448 Review.
-
Advances in smart delivery of food bioactive compounds using stimuli-responsive carriers: Responsive mechanism, contemporary challenges, and prospects.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021 Nov;20(6):5449-5488. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12851. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2021. PMID: 34668321 Review.
-
Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs): Advanced nanostructured materials to enhance the functional performance of food packaging materials.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 May;327:103153. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103153. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 38604082 Review.
-
Chitosan and its composites-based delivery systems: advances and applications in food science and nutrition sector.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(20):4579-4598. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.2004992. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 34793271 Review.
-
Proteins from leguminous plants: from structure, property to the function in encapsulation/binding and delivery of bioactive compounds.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(19):5203-5223. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1883545. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33569994 Review.
Cited by
-
Obtaining and Characterization of Nutraceuticals Based on Linoleic Acid Derivatives Obtained by Green Synthesis and Their Valorization in the Food Industry.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 24;17(15):2416. doi: 10.3390/nu17152416. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40806004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Patel A.R., Velikov K.P. Colloidal Delivery Systems in Foods: A General Comparison with Oral Drug Delivery. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011;44:1958–1964. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.04.005. - DOI
-
- Li R., Guo Y., Dong A., Yang X. Protein-Based Emulsion Gels as Materials for Delivery of Bioactive Substances: Formation, Structures, Applications and Challenges. Food Hydrocoll. 2023;144:108921. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108921. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

